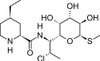
Pirlimycin is a semi-synthetic lincosamide prepared from clindamycin by hydrolysing the propyl N-methylproline and re-annealing a 4-ethylpipecolic acid. Pirlimycin is more hydrophobic than clindamycin and is more potent against a number of important pathogens. Like other members of the lincosamide family, pirlimycin is a broad spectrum antibiotic with activity against anaerobic bacteria and protozoans. Pirlimycin has been less extensively researched than the older lincosamides.
Pirlimycin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Good water solubility.
Pirlimycin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Good water solubility.
| Mechanism of Action | Pirlimycin acts by binding to the 23S ribosomal subunit, blocking protein synthesis. |
| Molecular Formula | C17H31ClN2O5S |
| Documents | Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of clindamycin analogues: pirlimycin,1,2 a potent antibacterial agent. Birkenmeyer R.D. et al. J. Med. Chem. 1984, 27, 216. In vitro activity of U-57930E, a new clindamycin analog, against aerobic gram-positive bacteria. Ahonkhai V.I. et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982, 21, 902. |