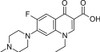
Pefloxacin Mesylate Dihydrate is a broad-spectrum, synthetic, third-generation fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Pefloxacin, an analog of Norfloxacin, was discovered in 1979. Pefloxacin, like other fluoroquinolones, inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase and Topoisomerase IV, which disrupts bacterial cell division. Novel derivatives of Pefloxacin were found to have anti-cancer properties. Quinolone-topoisomerase biology is a useful model to understand host-parasite interactions and investigate manipulation of the bacterial chromosome by topoisomerases.
Pefloxacin Mesylate Dihydrate is freely soluble in aqueous solution.
We also offer:
- Pefloxacin (P015)
| Mechanism of Action | Fluoroquinolone antibiotics like Pefloxacin target bacterial DNA gyrase, a type II topoisomerase enzyme which reduces DNA strain during replication. Because DNA gyrase is required during DNA replication, subsequent DNA synthesis and ultimately cell division is inhibited. This enzyme is the primary target for Gram-negative bacteria.
Pefloxacin inhibits topoisomerase IV, the primary target for Gram-positive bacteria. Since this enzyme is required to separate replicated DNA, the inhibition results in strand breakage of the bacterial chromosome, which ultimately inhibits DNA replication and transcription. |
| Spectrum | Pefloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic which targets a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms including a few Mycoplasma species such as M. bovis, M. tuberculosis, and M. africanum. |
| Impurity Profile | Impurity A| 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (demethylated pefloxacin or norfloxacin)|70458-96-7|C16H18FN3O3|319.331| Impurity B| 6-chloro-1-ethyl-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (chlorinated homologue of pefloxacin)||C17H20ClN3O3|349.81| Impurity E| 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)quinoline-4(1H)-one (decarboxylated pefloxacin)||C16H20FN3O|389.35| Impurity D| 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)-1-methylpiperazine 1-oxide (N-oxide of pefloxacin)|85145-21-7|C17H20FN3O4|349.36| Impurity C| 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (isopefloxacin)|70458-92-3|C17H20FN3O3|333.36| Impurity F| 7-chloro-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (N-ethyl acid) (norfloxacin impurity A)||C12H9ClFNO3|269.66| Impurity G| ethyl 7-chloro-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate (N-ethyl ester)|||| Impurity H| 5-chloro-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (iso-N-ethyl acid)| |
| Microbiology Applications |
Pefloxacin is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram- positive, Gram-negative, and Mycoplasma microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
|
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | Pefloxacin cytotoxicity in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes was evaluated and found to be hepatoxic at 400 mg/L (Nordmann et al, 1989). An investigation of Pefloxacin on human myelopoiesis in vitro was evaluated on cell cultures of mononuclear cells derived from human bone marrow samples and found it has no influence on the proliferation of human myeloid precursors at 0.5-50 µg/ml (Pallavicini et al, 1989). |
| Cancer Applications | The in vitro effect of Pefloxacin on growth of normal hematopoietic progenitor stem cells and on leukemic cell lines was investigated. It was found to have a dose-dependent inhibition of colony formation both from normal bone marrow cells and from the leukemic line K-562 cells and HL-60 cells when used at ≥ 25 µg/ml (Somekh et al, 1989).
An evaluation of Pefloxacin derivatives and their biological activity was screened against human Pc-3 cancer cell lines and the compounds demonstrated anti-cancer properties (Allaka et al, 2016). |
| Molecular Formula | C17H20FN3O3 · CH4O3S •2H2O |
| References |
Allaka T et al (2016) Design, synthesis and biological activity evaluation of novel Pefloxacin derivatives as potential antibacterial agents. Med. Chem. Res. 25(5):977-993 PMID 3000292 Drlica K and Zhao X (1997) DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV, and the 4-quinolones. Microbiol. Molec. Biol. Rev. MMBR 6(3):377-392 Nordmann P, Pechinot A and Kazmierczak A (1989) Cytotoxicity and uptake of Pefloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and ofloxacin in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 24(3):355-363 PMID 2808191 Pallavicini F, ANtinori A, Federico G, Fantoni M and Nervo P (1989) Influence of two quinolones, ofloxacin and Pefloxacin, on human myelopoiesis in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 33(1):122-123 PMID 2712545 Somekh E, Shaked N and Rubinstein E (1989) In vitro effects of Ciprofloxacin and Pefloxacin on growth of normal human hematopoietic progenitor cells and on leukemic cell lines. J. Pharmacol. and Exp. Ther. 248(1):415-418 PMID 2913285 |