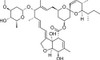
Avermectin monosaccharide is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Avermectins can modulate gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) chloride channels in vertebrate neurons. |
| Insect Biology Applications | Electrophysiological findings by injection of E. elegans mRNA into Xenopus laevis oocytes indicated that Avermectins act on glutamate-gated chloride channels in nematodes. |
| References | Blizzard T, Fisher MH, Mrozik H, Shih TL (1990) Avermectins and Milbemycins. In: Lukacs G, Ohno M. (eds) Recent Progress in the Chemical Synthesis of Antibiotics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg Chabala J.C. et al. (1980) Ivermectin, a new broad-spectrum antiparasitic agent. J. Med. Chem. 23:1134Chen TS, Inamine ES (1989) Studies on the biosynthesis of Avermectins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 270(2):521-5 PMID 2705778 Egerton JR et al (1979) Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: Efficacy of the B1a component. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 15(3):372-378 PMID 464563 Ikeda H and Omura S (1997) Avermectin biosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 97(7):2591-2610 Mrozik H. et al (1982) Avermectin aglycones. 47:489Pivnichny JV, Arison BY, Preiser FA, Shim JSK and Mrozik H (1988) Base-catalyzed isomerization of avermectins. J. Agric. Food Chem 36(4):826-828 Pivnichny JV, Shim JK and Zimmerman LA (1983) Direct determination of avermectins in plasma at nanogram levels by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Sci. 72(12):1447-1450 PMID 6663483 |