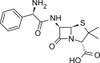
Ampicillin Sodium is a member of the β-lactam family structurally similar to penicillin. The compound inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Ampicillin resistance is used as a selectable marker to confirm successful cell transformation, as only cells containing plasmid-encoded ESBLs (Extended Spectrum B-lactamases) survive. Ampicillin Sodium is soluble in water.
We also offer: