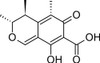
Citrinin is a quinonemethine mycotoxin produced by diverse fungi including Aspergillus and Penicillium. Citrinin has been extensively investigated and is a potent nephrotoxin with hepatoxic and teratogenic activity. Citrinin is the causative agent of Balkan nephropathy and yellow rice fever in humans. At the molecular level, citrinin exhibits a range of effects including free radical damage to DNA and disruption of mitochondrial membrane-bound enzymic activities and structural integrity. Specifically, citrinin is an inhibitor of NADH dehydrogenase in the mitochondrial electron transport chain and this action is responsible for recent reports of citrinin's apoptotic activity.
Citrinin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
Citrinin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.