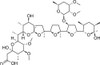
Maduramicin is a monovalent glycoside polyether ionophore antibiotic and broad-spectrum anticoccidial As a ionophore, it forms complexes with monovalent cations, with a higher affinity for K+ than Na+. Maduramicin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO but exhibits poor water solubility.
We also offer:
- Maduramicin Ammonium (M047)
| Application | Maduramicin can be used as a positive control in compound evaluation studies and as lead compounds for chemical optimization. |
| Mechanism of Action | Maduramicin can form complexes with cations (particularly Na+, K+ and Ca2+), thereby promoting their transport across the cell membrane and increasing the osmotic pressure in the coccidia, which inhibits certain mitochondrial functions such as substrate oxidation and ATP hydrolysis, eventually leading to protozoal cell death.
In cell culture studies, Maduramicin was found to cause accumulation of the cells at G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle, and induces cellular apoptosis. It can also downregulate protein expression of cyclin D1, cyclin-dependent kinases, and upregulate expression of CDK inhibitors. |
| Spectrum | It is effective against Gram-positive bacteria, and exhibits a broad spectrum of anticoccidial activity against the most frequently occurring Eimeria species, and is also active against Cryptosporidium and Treponema. |
| Microbiology Applications | Maduramicin is currently used to combat coccidiosis in poultry. |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | Using mouse myoblasts (C2C12) and human rhabdomyosarcoma (RD and Rh30) cells as an experimental model, Maduramicin was found to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in a dose-dependent fashion.
A chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) was developed to detect Cryptosporidium parvum growth in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell cultures. Maduramicin was found to have selective activity against C. parvum in a dose-dependent manner. CLIA offers advantages over conventional enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunofluorescence assay methods in that it is more sensitive and efficient. It is an efficient tool for evaluating potential anti-cryptosporidial compounds prior to testing in animal models. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO but poor water solubility |
| Source | <em>Actinomadura yumaensis</em> (formerly <em>Nocardia</em> sp. X-14868 |
| References |
Chen X et al (2014) Maduramicin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in myoblast cells. PloS One. 9(12):e115652 Liu CM et al (1983) Novel polyether antibiotics X-14868A, B, C, and D produced by a Nocardia. Discovery, fermentation, biological as well as ionophore properties and taxonomy of the producing culture. J. Antibiot. 36:343Maxim I et al (2016) Maduramicin rapidly eliminates malaria parasites and potentiates the gametocytocidal activity of the pyrazoleamide PA21A050. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother 60(3): 1492-1499 Mead JR et al (1995) Evaluation of Maduramicin and alborixin in a SCID mouse model of chronic cryptosporidiosis. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 39 (4) 854-858 You X et al (1996) A chemiluminescence immunoassay for evaluation of Cryptosporidium parvum growth in vitro. FEMS Microbiol Lett 136(3):251-256 |