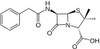
Penicillin G Potassium, USP is a member of the β-lactam antibiotics and was one of the first discovered antibiotics.
Penicillin G potassium is sparingly soluble in aqueous solution.
Click here for more Penicillin products.
| Mechanism of Action | β-lactams interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to β-lactams is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum |
Penicillin is targets primarily Gram-positive bacteria including Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species. |
| Microbiology Applications | Penicillin is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options for infected patients. Representative MIC values include:
Mycoplasma Media SupplementsPenicillin can be used as a selective agent in several types of isolation media: Mycoplasma Agar - Mycoplasma Supplement G Mycoplasma Agar - Mycoplasma Supplement P |
| Plant Biology Applications | In a study by Windsor et al. (1972), Penicillin G Potassium was shown to control the bacterial plant disease clover club leaf in crimson clover using 100 – 1000 µg/mL. |
| Molecular Formula | C16H17KN2O4S |
| References |
Guzmán, Flavio, MD (2008) Beta lactam antibiotics (penicillins and Cephalosporins) Mechanism of Action.” Med. Pharmacol. Pharmacology Corner. Pitout JD, Sanders CC, Sanders WE Jr. Antimicrobial resistance with focus on beta-lactam resistance in Gram-negative bacilli. Am J Med 1997; 103:51 |