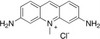
Acriflavine Hydrochloride (syn: Acriflavine HCl) is the hydrochloride salt of Acriflavine, a mixture of 3,6-diamino-10-methylacridium (acriflavin) and 3,6-diaminoacridine (proflavin). It was developed in 1912 by Paul Ehrlich, a medical researcher from Germany. It is a fluorescent dye commonly used as a topical contrast agent. It stains cell nuclei and is applied to tissues before miscrocopy. Acroflavine has been used in confocal laser endomicroscopy. The compound has also been used for strain selection.
Acriflavine HCl has both antimicrobial and antiviral properties, and is a potent papain-like protease (PLpro) inhibitor, which inhibits SARS-CoV-2A and other betacoronaviruses. Acriflavine Hydrochloride is freely soluble in aqueous solution.
This product is considered a dangerous good. Quantities above 1 g may be subject to additional shipping fees. Please contact us for questions.
| Mechanism of Action | Acriflavine toxicity arises from its ability to bind to and intercalate DNA. DNA intercalation leads to numerous errors which have a lethal effect on targeted organisms. |
| Microbiology Applications | Acriflavine has been used in RNA fluorescent labeling applications by RNA hydrolysis using HCl. It has aslo been used in Neurospora strain selection by reviewing the resistance to acriflavine. |
| Cancer Applications | Acriflavine has been shown to inhibit HIF-1, a heterodimeric transcription factor which responds to hypoxia and facilitates further cancer progress. Acriflavine prevents dimerization of HIF-1 to prevent its role in cancer growth. |
| Molecular Formula | C13H11N3 and C14H14N3 •HCl |
| References |
Kawai M and Yamagishi J (2009) Mechanisms of action of Acriflavine: Electron microscopic study of cell wall changes induced in Staphylococcus aureus by Acriflavine. Microbiol. Immunol. 53(9):481-486 PMID 19703241 Lee K et al (2009) Acriflavine inhibits HIF-1 dimerization, tumor growth, and vascularization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106 (42):17910-17915 PMID 19805192 Levinson JW, Maher VM and McCormick JJ (1979) Fluorescent labeling of fragments of high molecular weight RNA. Anal. Biochem. 93(2):399-406 Acriflavine, a clinically aproved drug, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and other betacoronaviruses. |
| MIC | Escherichia coli| 2 - 128|| Klebsiella pneumonia| 128 - 512|| Staphylococcus aureus| 3.13 - 50|| |