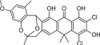
Bischloroanthrabenzoxocinone ((-)BABX) is a selective inhibitor of Type II fatty acid synthesis (FASII). BABX showed IC50 values of 11.4 and 35.3 µg/ml in the S. aureus and E. coli FASII assays, respectively, with comparable antibacterial activities. FASII is essential to bacterial cell viability and is a promising target for the development of novel antibiotics.
Bischloroanthrabenzoxocinone is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
Bischloroanthrabenzoxocinone is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | BABX has been shown to inhibit agonist binding to Liver X receptors (LXR). These receptors regulate the expression of the ABCA1 gene, which mediates the efflux of cholesterol from cells. |
| Molecular Formula | C28H24O7Cl2 |
| References | Determination of selectivity and efficacy of fatty acid synthesis inhibitors. Kodali S. et al. , J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1669. Anthrabenzoxocinones from Streptomyces sp. as Liver X receptor ligands and antibacterial agents. Herath K. B. et al. , J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1437. |