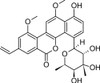
Chrysomycin A is the major analogue in a complex of C-glycoside antitumor actives isolated from Streptomyces. Chrysomycin A, with a vinyl group in the 8-position, is the most potent analogue of the complex, and is thought to act as an inhibitor of the catalytic activity of human topoisomerase II. Chrysomycin A has a potent antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and antitumor profile.
Chrysomycin A is soluble in DMF and DMSO and is moderately soluble in methanol or ethanol.
Chrysomycin A is soluble in DMF and DMSO and is moderately soluble in methanol or ethanol.
| Mechanism of Action | The mechanism of action of chrysomycins is not fully understood; however, recent research suggests chrysomycins may act as photoactivated cross-linkers of DNA to histones. |
| References | Biochemical characterisation of elsamicin and other coumarin-related antitumor agents as potent inhibitors of human topoisomerase II. Lorico A. et al. Eur. J. Cancer. 1993, 29A, 1985 Chrysomycin derivative compounds and use as antitumor agents. US Patent 6,030,951, 2000. Histone H3 and heat shock protein GRP78 are selectively cross-linked to DNA by photoactivated gilvocarcin V in human fibroblasts. Matsumoto A. et al. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3921. |