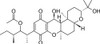
Cochlioquinone A is the major component of a bioactive pigment isolated from Bipolaris leersia. Cochlioquinone A is anti-angiogenic and exhibits inhibitory activity against diacylglycerol acyltransferase and NADH-ubiquinone reductase.
Cochlioquinone A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
Cochlioquinone A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Cochlioquinone A is an antagonist of the human chemokine receptor, CCR5, in HIV-1. |
| References | Cochlioquinones and epi-cochlioquinones: antagonists of the human chemokine receptor CCR5 from Bipolaris brizae and Stachybotrys chartarum. Yoganathan K., et al. , J. Antibiot. 2004, 57, 59. Cochlioquinone A1, a new anti-angiogenic agent from Bipolaris zeicola. Jung H.J. et al. , Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 4743. Inhibitory activity of diacylglycerol acyltransferase by cochlioquinones A and A1. Lee H.B. et al. , J. Antibiot. 2003, 56, 967. Phytotoxic compounds cochlioquinones are inhibitors of mitochondrial NADH-ubiquinone reductase. Lim C.-H. et al. , J. Pesticide Sci. 1996, 21, 213. |