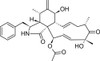
Cytochalasin D is the most studied of the cytochalasins. Like most of the members of this mycotoxin class, cytochalasin D exhibits potent inhibition of actin filament function leading to cell death by apoptosis. This led to early investigation of the metabolite as an antitumor agent. Cytochalasin D has become one of the standard cellular probes for investigating the role of actin in cell biology.
Cytochalasin D is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
Cytochalasin D is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Cytochalasin D exhibits potent inhibition of actin filament function leading to cell death by apoptosis. |
| References | Antitumor activity of cytochalasin D: Katagiri K. and Matsuura S. J. Antibiot. 1971, 24, 722. Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin: Cooper J. A. J. Cell. Biol. 1987, 105, 1473 Myosin-actin interaction plays an important role in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 release from host cells. H. Sasaki, H. et al. ; PNAS 1995, 92, 2026. Disruption of actin microfilaments by cytochalasin D leads to activation of p53. Rubtsova S. N. et al. , FEBS Lett. 1998, 430, 353. |