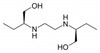
Ethambutol is a unique antitubercular antibiotic which inhibits cell wall formation in Mycobacterium species. It inactivates arabinosyl transferase, an enzyme that transports mycolic acids to the Mycobacterium cell wall. It was discovered in 1961 by Lederle Labs. Ethambutol exists in three different sterioisomeric forms: the enantiomeric pair referred to as (+)-(S,S)- and (-)-(R,R)-ethambutol, along with the achiral sterioisomer called the meso-form. It is the (+)-(S,S)-enantiomer that has the antitubercular activity.
Ethambutol is slightly soluble in water.
| Mechanism of Action | Ethambutol inactivates arabinosyl transferase, an enzyme responsible for transporting mycolic acids to the cell wall. Without this enzyme, cell permeability is increased leaving the oraganism vulnerable to toxic matter. |
| Spectrum | Ethambutol targets primarily species of the Mycobacterium genus including Mycobacterium tuberculosis. |
| Molecular Formula | C10H24N2O2 |
| Microbiology Applications |
Ethambutol is bacteriostatic against actively growing tuberculosis bacilli. Mutations among embCAB operon are responsible for around 70% clinical ethambutol-resistant M. tuberculosis (Xiang et al, 2020). Researchers found that pairing β-lactams with ethambutol significantly improves their efficacy against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The presence of Ethambutol enhances β-lactam access through the cell wall, which may translate into a prolonged contact between the compound and its targets at a concentration that effectively kills the pathogen. Authors used the THP-1 cell line and indicated that it will be important to validate results in alternative systems such as primary cells ie human macrophages obtained from peripheral blood-derived monocytes and co-cultures with lymphocytes from the same donor, ensuring a broader applicability of their findings (2024). |
| References |
Landau R, Achilladelis B, Scriabine A (1999). Pharmaceutical Innovation: Revolutionizing Human Health. Chemical Heritage Foundation. p. 171. ISBN 9780941901215 2024) Ethambutol and meropenem/clavulanate synergy promotes enhanced extracellular and intracellular killing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 68:e01586-23 Xiang X, Gong Z, Deng W, Sun Q and Xie J (2020) Mycobacterial Ethambutol responsive genes and implications in antibiotics resistance. J Drug Targeting 29(3):284–293 |