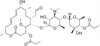
Midecamycin is an naturally occurring, broad-spectrum acetoxy-substituted macrolide antibiotic similar in structure to erythromycin. An acetoxy group is substituted on position 9 of the 16-membered ring and on position 4 of the terminal sugar. It is naturally produced by Streptomyces mycarofaciens. It interrupts protein synthesis of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Its metabolites present little to no antimicrobial activity. It is very soluble in methanol, ethanol, and acidic solutions and soluble in DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Midecamycin inhibits bacterial growth by targeting the 50S ribosomal subunit preventing peptide bond formation and translocation during protein synthesis. Resistance to Midecamycin is commonly attributed to mutations in 50S rRNA preventing Midecamycin binding allowing the cell to synthesize proteins free of error. |
| Spectrum | Midecamycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic targeting a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria especially those which cause respiratory, ear, and skin infections. It is active against Streptococci, Staphylococci, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, and Bordetella pertussis. |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | In vitro research of Midecamycin showed immunosuppressive properties by inhibiting T-cell responses via suppressing IL-2. These results suggest potential application for post-transplant complications and inflammatory diseases. |
| References |
Lovmar M and Tenson T (2003) The mechanism of action of macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramin B reveals the nascent peptide exit path in the ribosome.. J. Molec. Microbiol. 330 (5):1005-1014 PMID 12860123 Morikawa K (1994) Immunomodulatory effects of three macrolides, Midecamycin Acetate, Josamycin, and Clarithromycin, on human T-lymphocyte function in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 38(11): 2643-2647 PMID 7532933 Neu HC (1983) In vitro activity of Midecamycin, a new macrolide antibiotic. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 24(3):443-444 PMID 6639001 |