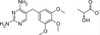
Trimethoprim Lactate is a synthetic derivative of trimethoxybenzyl-pyrimidine with bacteriostatic and antiprotozoal properties. As a pyrimidine inhibitor of bacterial dihydrofolate reductase, Trimethoprim binds tightly to the bacterial enzyme, blocking the production of tetrahydrofolic acid from dihydrofolic acid, arresting folic acid synthesis.
When Trimethroprim Lactate is combined with sulfonamides like Sulfamethoxazole (S045) the compounds show bactericidal effects, but are only bacteriostatic when used separately. The activity is attributed to their synergistic effect in inhibiting folic acid metabolism in bacteria and thus blocking nucleotide biosynthesis.
Trimethoprim Lactate is broad-spectrum and is active against most Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria, including Nocardia, Brucella, Gram-negative bacilli, and some Gram-positive bacteria like Streptococcus, Toxoplasma and some other coccidians. It is active against the bacteria causting cystitis, mild acute prostatitis, and urinary tract infections. The compound is used as a selection agent in research applications.
Trimethoprim Lactate is freely soluble in aqueous solution.
We also offer:
- Trimethoprim (T011)
| Mechanism of Action |
Trimethoprim Lactate acts by interfering with the action of bacterial dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) and inhibits the reduction of dihydrofolic acid (DHF) to tetrahydrofolic acid (THF) thus inhibiting synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid. Tetrahydrofolic acid is an essential precursor in the de novo synthesis of the intermediate Thymidine monophosphate (dTMP), precursor of DNA metabolite Thymidine triphosphate thus interference with this pathway inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis. The activity of this compound may depend on the extent to which the processes of either catabolism or folic acid production occur in different bacteria (Weir and Scott, 2000). |
| Spectrum | Trimethoprim Lactate has a wide antibacterial spectrum and is active against most Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria, including Nocardia, Brucella, Gram-negative bacilli, and some Gram-positive bacteria like Streptococcus, Toxoplasma and some other coccidians. |
| Microbiology Applications | Trimethoprim Lactate is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
|
| Plant Biology Applications | Trimethoprim Lactate can be used in combination with rifampicin to provide sufficient activity against pathogenic microbes. When used without other supplemental antibiotics, trimethoprim was not shown to provide sufficient activity (Pollock et al, 1983). |
| Molecular Formula | C14H18N4O3 · C3H6O3 |
| References |
Kneifel W and Leonhardt W (1992) Testing of different antibiotics against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria isolated from plant tissue culture. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 29:139-144 Pollock K, Barfield DG and Shields R (1983) The toxicity of antibiotics to plant cell cultures. Plant Cell Rep. 2:36-39 PMID 24257853 Tiwari KN, Tiwari V, Singh J et al (2012) Synergistic effect of Trimethoprim and bavistin for micropropagation of Bacopa monniera. Biol. Plant 56:177–180 Weir, DG and J. Scott J (2000) Mechanism of the antimicrobial drug Trimethoprim revisited. FASEB J 14(15):2519-2924 PMID 11099470 |