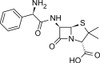
Ampicillin Trihydrate, USP is a member of the β-lactam family similar in structure to penicillin. Ampicillin Trihydrate is slightly soluble in water (10 mg/mL) and soluble in 1 N HCl (50 mg/mL).
We also offer:
- Ampicillin/Sulbactam (2:1) (A071)
- Ampicillin Anhydrous (A043)
- Ampicillin Sodium (A042)
- Ampicillin Trihydrate, EP (A020)
Ampicillin Trihydrate, USP conforms to United States Pharmacopoeia specifications.