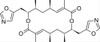
Conglobatin is a unique dimeric macrolide antibiotic derived from ionomycin, an ionophore produced by Streptomyces conglobatus. Conglobatin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Macrolide antibiotics inhibit bacterial growth by targeting the 50S ribosomal subunit preventing peptide bond formation and translocation during protein synthesis. |
| Molecular Formula | C28H38N2O6 |
| References | Westley, John W., and Ralph H. Evans. "The Journal of Antibiotics." Conglobatin, A Novel Macrolide Dilactone from Streptomyces Conglobatus ATCC 31005 32.0 (1979): 874-77. Ncbi.gov. Web. 25 Feb. 2013. |