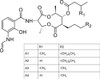
Antimycin (syn: Antimycin A) is a complex of related macrocyclic lactones, predominantly A1 to A4, isolated from several species of Streptomyces, first reported in the early 1950s for potent antifungal activity. There are over 20 known analogs in the Antimycin A class, mostly involving variation of the fatty acid ester chain length or adjacent alkyl starting unit. Antimycin A is widely used as a bioprobe of respiration and other applications.
Antimycin A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
We also offer:
| Mechanism of Action | Antimycin A binds to cytochrome C reductase at the Qi site, inhibiting the oxidation of ubiquinol to ubiquinone. |
| Molecular Formula | C28H40N2O9 (for A1) |
| References |
Bryant R and Dunshee BR et al (1949) The isolation and properties of Antimycin A. B Am. Chem. Soc. 71:2436 Yan Y et al (2012) Biosynthetic pathway for high structural diversity of a common dilactone core in antimycin production. Org. Lett. 14:4142 |