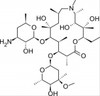
Azithromycin impurity E, EvoPure® (Aminoazithromycin) is one of several impurities found in Azithromycin and can be used as a reference standard for impurity profiling.
We also offer:
- Azithromycin impurity F, EvoPure® (A075)
- Azithromycin impurity G, EvoPure® (A083)
- Azithromycin impurity H, EvoPure® (A084)
- Azithromycin impurity I, EvoPure® (A081)
- Azithromycin impurity J, EvoPure® (A082)
- Azithromycin impurity L, EvoPure® (A078)
EvoPure® products have been fully characterized by spectral analysis and are shipped with a comprehensive certificate of analysis containing lot-specific HPLC, MS, HNMR, and FTIR data.
| Application | Azithromycin impurity E is primarily used as a reference standard. Reference standards are well characterized compounds that can be used to help identify and/or quantify impurities in pharmaceutical compounds and antimicrobials. |
| Mechanism of Action | Azithromycin inhibits bacterial growth by binding to the 70S ribosome (specifically the 50S subunit) preventing peptide bond formation and translocation during protein synthesis. Resistance is attributed to mutations in 50S rRNA preventing binding of Azithromycin and allowing the cell to synthesize error-free proteins. |
| Molecular Formula | C36H68N2O12 |
| References | Gladue RP, Bright GM, Isaacson RE and Newborg MF (1989) In vitro and in vivo uptake of Azithromycin (CP-62,993) by phagocytic cells: Possible mechanism of delivery and release at sites of infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33(3):277-282 PMID 2543276 Lovmar, M and Tenson T (2003) The mechanism of action of macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramin B reveals the nascent peptide exit path in the ribosome. J. Molec. Microbiol. 330 (5):1005-1014 PMID 12860123 Wolf K and Malinverni R (1999) Effect of Azithromycin plus rifampin versus that of Azithromycin alone on the eradication of Chlamydia pneumoniae from lung tissue in experimental pneumonitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43(6): 1491-1493 PMID 10348778 |