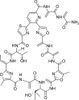
Berninamycin A is an antibiotic discovered in 1976 from a strain of Streptomyces. Berninamycin A is a macrocyclic 'peptide' comprising atypical amino acids linked to thiazole and oxazoles. Berninamycin A is closely related to siomycin, a recently discovered inhibitor of oncogenic transcription factor, FoxM1.
Berninamycin A is soluble in DMF and DMSO.
Berninamycin A is soluble in DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Chemically very complex, berninamycin A is an inducer of tipA, a gene that controls the bacterial transcription regulators, TipAL and TipAS, that are central to multidrug resistance. |
| Molecular Formula | C51H51N15O15S |
| References | Berninamycin. I. The structure of berninamycinic acid. Liesch, J.M. et al. , J.Am.Chem.Soc. 1976, 98, 299. Mode of action of berninamycin. An inhibitor of protein biosynthesis. Reusser F. Biochem. 1969, 8, 3303. Identification of a chemical inhibitor of the oncogenic transcription factor Forkhead Box M1. Radhakrishnan et al. , Cancer Res. 2006, 19, 9731. |