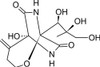
Bicyclomycin is a polar metabolite first isolated from Streptomyces sapporonensis in 1972. The selective Gram negative profile of bicyclomycin is rare among Streptomyces metabolites.
Bicyclomycin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
Bicyclomycin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | The primary site of action for bicyclomycin is thought to be the rho transcription termination factor. |
| Molecular Formula | C12H18N2O7 |
| References | Bicyclomycin, a new antibiotic I. Taxonomy, isolation and characterization. Miyoshi T. et al. J. Antibiot. 1972, 25, 569. Bicyclomycin, a new antibiotic II. Structural elucidation and acyl derivatives. Kamiya T. et al. J. Antibiot. 1972, 25, 576. Transcription termination factor rho: The site of bicyclomycin inhibition in Escherichia. Zwiefka A. et al. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 3564. |