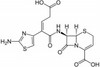
Ceftibuten is a third generation cephalosporin antibiotic. It has exceptional β-lactamase stability and is resistant to inactivation by most β-lactamases made by common Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Ceftibuten can be used to study drug resistance and transport pathways. Ceftibuten is freely soluble in aqueous solution and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Like β-lactams, cephalosporins interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to cephalosporins is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum | Ceftibuten is a broad-spectrum antibiotic targeting a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. |
| Microbiology Applications |
Ceftibuten is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
|
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | Ceftibuten uptake in human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco‐2) cells growing on transwells was studied, and authors found that uptake involves multiple transport pathways. Since cells are polarized, with an apical end and a basolateral end, the apical transport system was found to be different. Apical uptake is mediated by an energy-dependent carrier and energy-independent facilitated diffusion (Menon and Barr 2002). |
| Molecular Formula |
C15H14N4O6S2 |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in aqueous solution and DMSO |
| Impurities | Single Impurity: ≤1.0% Total Impurities: ≤2.0% |
| References | Debbia EA, Schito CG and Pesce A (1991) Antibacterial activity of Ceftibuten, a new oral third generation cephalosporin. J. Chemother 3(4): 209-225 Georgopapadakou, NH (1992) Mechanisms of action of cephalosporin 3'-quinolone esters, carbamates, and tertiary amines in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37(3): 59-65 Jones RN and Barry AL (1988) Antimicrobial activity, spectrum, and recommendations for disk diffusion susceptibility testing of ceftibuten (7432-S; SCH 39720), a new orally administered cephalosporin. Antimicrob. Agents and Chemother. 32 (10) 1576-1582 Jones RN (1995) A review of antimicrobial activity, spectrum and other microbiologic features. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 14(7):S77-83 PMID 7567314 Menon RM and Barr WH (2002) Transporters involved in apical and basolateral uptake of ceftibuten into Caco-2 cells. Biopharmaceutics and Drug Disposition. 23(8):317-326 Owens RD, Nightingale CH and Nicolau DP (1997) Ceftibuten: An overview. Pharmacother. 17(4):707-720 PMID 9250548 Perilli M et al (2007) In vitro selection and characterization of mutants in TEM-1-producing Escherichia coli by ceftazidime and ceftibuten. J Chemother 19(2):123-126 PMID 17434819 Wise R, Andrews JM, Ashby JP and Thornber D (1990) In-vitro activity against respiratory pathogens, β-lactamase stability and mechanism of action, J. Antimicrob Chemother. 26 (2): 209–213 PMID 2120175 |
| MIC | Bacteroides bivius| 64 - >64|| Bacteroides disiens| 64 - >64|| Bacteroides distasonis| 64 - >64|| Bacteroides fragilis| 4 - >128|| Bacteroides ovatus| 64 - >64|| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 64 - >64|| Bacteroides vulgatus| 64 - >64|| Borrelia burgdorferi S.L.| 4 - 32|| Branhamella catarrhalis| 0.06 - 16|| Brucella melitensis| 8|| Brucella suis| 8|| Citrobacter freundii| 0.06 - 64|| Citrobacter spp.| 0.12 - >32|| Clostridium difficile| >64 - >128|| Clostridium histolyticum | 1 - >64|| Clostridium perfringens| 1 - >64|| Clostridium sordellii| 1 - >64|| Clostridium sporogenes| 1 - >64|| Clostridium spp.| 2.275|| Edwardsiella hoshinae | ≤0.03|| Edwardsiella ictaluri | ≤0.03 - 0.5|| Edwardsiella tarda| ≤0.03 - 1|| Enterobacter aerogenes| 0.25 - >64|| Enterobacter cloacae| 0.03 - >128|| Enterobacter sakazakii| 0.015 - 6|| Enterobacter spp.| 0.03 - >32|| Enterococcus| >32|| Enterococcus faecalis| >64 - >128|| Enterococcus faecium| >64 - >128|| Enterococcus liquefaciens | >64|| Escherichia coli| 0.015 - >32|| Haemophilus influenzae| 0.015 - 1|| Haemophilus parainfluenzae| 0.03 - 0.06|| Hafnia alvei| 0.25 - 1|| Helicobacter pylori| 2 - 8|| Klebsiella oxytoca (ceftazidime-resistant)| 0.03 - 0.25|| Klebsiella pneumoniae| 0.03 - 0.25|| Klebsiella spp.| 0.008 - >32|| Listeria innocua| ≥64|| Listeria ivanovii| ≥64|| Listeria monocytogenes| ≥64|| Listeria seeligeri| ≥64|| Listeria welshimeri| ≥64|| Moraxella catarrhalis| 0.5 - 4|| Morganella morganii| 0.008 - >32|| Neisseria gonorrhoeae| 0.015 - 0.5|| Peptococcus asaccharolyticus| 1.861|| Peptostreptococcus spp.| 6.625|| Proteus mirabilis| 0.002 - 16|| Proteus vulgaris| 0.008 - 8|| Providencia rettgeri| 0.03 - 0.13|| Providencia spp.| 0.004 - 16|| Providencia stuartii| 0.03 - 0.6|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| 16 - >64|| Pseudomonas cepacia| 0.25 - >64|| Pseudomonas fluorescens | 8 - >64|| Pseudomonas putida| 8 - >64|| Pseudomonas spp.| 2 - >32|| Pseudomonas stutzeri| 8 - >64|| Salmonella Agona| 0.03|| Salmonella Brandenburg| 0.03|| Salmonella Enteritidis| 0.03|| Salmonella spp.| 0.03 - >32|| Salmonella typhimurium| 0.03|| Serratia liquefaciens| 0.06 - 8|| Serratia marcescens| 0.06 - 32|| Serratia spp.| 0.06 - 32|| Shigella flexneri| 0.06 - 0.25|| Shigella sonnei| 0.06 - 3.224|| Shigella spp.| 0.03 - 0.25|| Staphylococci | 12.8|| Staphylococcus aureus| 8 - >128|| Staphylococcus cohnii| >64|| Staphylococcus epidermidis| 4 - >128|| Staphylococcus haemolyticus| 8 - >64|| Staphylococcus hominis| 8 - >64|| Staphylococcus saprophyticus| 8 - >128|| Staphylococcus simulans| 16 - >64|| Staphylococcus warneri| 8 - 32|| Streptococci| 0.25 - 16|| Streptococcus agalactiae| 16 - 32|| Streptococcus milleri| 4 - 64|| Streptococcus mitior| 2 - 64|| Streptococcus pneumonia| 0.5 - >256|| Streptococcus pyogenes| 0.5|| Streptococcus spp. (Viridans group)| 12.8|| Xanthomonas maltophilia| 0.5 - >64|| Yersinia enterocolitica| 0.06 - 8|| |