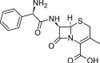
Cephalexin Hydrate is a broad-spectrum, first-generation cephalosporin that interferes wtih bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis. It can be used to study the effect of penicillin-binding proteins on bacterial cell well synthesis. The compound is formulated as the monohydrate. The product is slightly soluble in aqueous solution.
| Mechanism of Action | Like β-lactams, cephalosporins interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to cephalosporins is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum | Cephalexin Hydrate is a broad-spectrum antibiotic targeting a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria especially those which cause respiratory infections. |
| Microbiology Applications |
Cephalexin Hydrate is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
In vitro degradation of Cephalexin Monohydrate and its effect on MIC and MBC was studied using the broth microdilution method. Cephalexin was among the most degraded compounds tested, which has implications for determination of MIC for slow-growing bacteria (Lallemand et al, 2016). |
| Molecular Formula | C16H17N3O4S · H2O |
| Molecular Weight |
365.41 |
| References | Georgopapadakou NH (1992) Mechanisms of action of cephalosporin 3'-quinolone esters, carbamates, and tertiary amines in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37(3):559-565 Lallemand EA et al (2016) In vitro degradation of antimicrobials during use of broth microdilution method can increase the measured minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations. Front Microbiol. 7:2051 PMID 28066372 |
| MIC | Bacteroides bivius| 32|| Bacteroides distasonis| 32|| Bacteroides fragilis| 4 - >128|| Bacteroides melaninogenicus| 32|| Bacteroides ovatus| 32|| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 32|| Bacteroides vulgatus| 32|| Branhamella catarrhalis| 2 - 8|| Citrobacter diversus| 6.5|| Citrobacter freundii| 8 - 2048|| Clostridium bifermentans| 32|| Clostridium difficile| 32|| Clostridium perfringens| 32|| Clostridium ramosum| 32|| Clostridium sporogenes| 32|| Clostridium spp.| 32|| Diplococcus pneumoniae| 0.2 - 12.5|| Enterobacter| 50 - >100|| Enterobacter aerogenes| 32|| Enterobacter agglomerans| 8|| Enterobacter cloacae| 16 - 2048|| Enterobacter spp.| 4 - >128|| Enterobacteriaceae| 0.25 - 128|| Enterococci| 32|| Enterococcus faecalis| >32 - 128|| Escherichia coli| 0.78 - 512|| Haemophilus influenzae| 4 - >128|| Haemophilus spp.| 1 - 128|| Helicobacter pylori| 0.03 - 32|| Klebsiella oxytoca| 3.5|| Klebsiella pneumonia| 0.78 - 100|| Klebsiella spp.| 2 - >128|| Lactobacillus reuteri| 90|| Morganella morganii| 0.5 - >2048|| Neisseria gonorrhoeae| 0.25 - 32|| Neisseria meningitidis| 1|| Nocardia asteroides| 25 - ≥400|| Peptococcus asaccharolyticus| 32|| Peptostreptococcus anaerobius| 32|| Proteus mirabilis| 1 - >128|| Proteus morganii| 115.9|| Proteus rettgeri| 60.1|| Proteus spp. (indole-positive)| 2 - >128|| Proteus vulgaris| 0.12 - 512|| Providencia rettgeri| 32|| Providencia spp.| 0.12 - >128|| Providencia stuartii| 32|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| 32 - >256|| Pseudomonas cepacia| 32|| Pseudomonas flourescens| 32|| Pseudomonas putida| 32|| Pseudomonas spp.| >128 - >256|| Pseudomonas stutzeri| 32|| Salmonella| 0.8 - 3.12|| Serratia marcescens| 32 - >2048|| Serratia spp.| 2 - >128|| Staphylococci| 0.5 - 128|| Staphylococcus aureus| 0.78 ->128|| Staphylococcus epidermidis| 0.5 - 32|| Staphylococcus intermedius| 2|| Staphylococcus pseudintermedius| 0.5 - 8|| Staphylococcus saprophyticus| 1 - 128|| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia| 32|| Streptococcus agalactiae| 2|| Streptococcus pneumonia| 0.5 - 16|| Streptococcus pneumonia| 0.78 - 3.12|| Streptococcus pyogenes| 0.2 - 12.5|| Xanthomonas campestris pv. mangiferaeindicae (Xm)| 256 - >512|| |