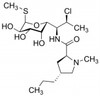
Clindamycin Phosphate (Clindamycin-2-phosphate) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic and antiparasitic agent. It is a semi-synthetic derivative of Lincomycin, a natural lincosamide from Streptomyces lincolnensis. Clindamycin Phosphate is freely soluble in water.
We also offer:
| Mechanism of Action | Lincosamides inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding the 50S ribosomal subunit and interfering with tRNA activity during translation. |
| Spectrum | Clindamycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic targeting primarily Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria such as Clostridium and Bacteroides species. It is also effective against protozoa. |
| Microbiology Applications | Clindamycin is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative anaerobes. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative concentration ranges include:
For representative MIC data, click here. |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | HIV-infected cells (MOLT3 cells) were incubated with increasing concentrations of Clindamycin with no impact on cell death (Wijsman et al, 2013). The effects of Clindamycin and its metabolites on mammalian cell lines (mouse leukemia L1210, human oral carcinoma KB, human acute myelogenous leukemia RPMI 6410, and human lymphocyte RPMI 1788) were evaluated. Metabolites clindamycin sulfoxide and clindamycose were nontoxic, whereas N-demethyl clindamycin showed cytotoxic effects in culture (Li et al, 1977). |
| Molecular Formula | C18H34ClN2O8PS |
| References | Dhawan VK and Thadepalli H (1982) Clindamycin: A review of fifteen years of experience. Clin. Infect. Dis. 4(6):1133-1153 PMID 6818656 Li LH, Kuentzel K L, Shugars KD and Bhuyan BK (1977) Cytotoxicity of several marketed antibiotics on mammalian cells in culture. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 30(6):506-512 PMID 560364 Lovmar M and Tanel T (2003) The mechanism of action of macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramin B reveals the nascent peptide exit path in the ribosome. J. Molec. Microbiol. 330(5 ): 1005-014 PMID 12860123 Magerlein BJ et al (1966) Chemical modification of lincomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 6:727 PMID 5985307 Wijsman JA, Dekaban GA and Rieder MJ (2013) Differential toxicity of reactive metabolites of Clindamycin and sulfonamides in HIV-infected cells: Influence of HIV infection on clindamycin toxicity in vitro. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 45(3):346-351 PMID 15703369 |
| MIC | Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans| 16 - ?| 821| Bacillus circulans| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Bacillus spp.| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Bacillus spp.| 0.5 - >2| 462| Bacillus thetaiotaomicron| 0.5 - >128| 982| Bacteroides bivius| ? - ?| 1385| Bacteroides bivius| <=0.062 - ?| 1470| Bacteroides caccae| <=0.5 - >125| 1476| Bacteroides caccae| ≤0.06 - >256| 497| Bacteroides caccae| 0.25 - >128| 1475| Bacteroides capillosus| ≤0.03 - 2| 818| Bacteroides capillosus| 0.5 - ?| 1470| Bacteroides distasonis| 0.03 - >128| 248| Bacteroides distasonis| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides distasonis| <=0.06 - >256| 1468| Bacteroides distasonis| <=0.062 - 4| 1470| Bacteroides distasonis| 0.5 - 8| 1469| Bacteroides distasonis| ≤0.06 - >256| 497| Bacteroides distasonis| 0.03 - >32| 1466| Bacteroides distasonis| 0.03 - >16| 1474| Bacteroides distasonis| <=0.03 - >128| 1477| Bacteroides distasonis| 0.5 - >64| 1473| Bacteroides distasonis (ATCC 8503)| 0.06 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides eggerthii| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides eggerthii (ATCC 27754)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.03 - >128| 248| Bacteroides fragilis| ≤0.004 - >128| 340| Bacteroides fragilis| <=0.03 - >128| 1475| Bacteroides fragilis| ? - ?| 381| Bacteroides fragilis| ≤0.12 - >16| 462| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.125 - 4| 1470| Bacteroides fragilis| ? - ?| 1385| Bacteroides fragilis| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.06 - >32| 1466| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.125 - 8| 1473| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.125 - >16| 1474| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.25 - 4| 1279| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.125 - >128| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis| <=0.06 - >256| 1468| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.125 - >256| 497| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.5 - >32| 1469| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.5 - >8| 1467| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.015 - 2| 401| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.5 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis| 0.5 - ?| 1474| Bacteroides fragilis (1995)| 0.5 - >256| 297| Bacteroides fragilis (1996)| ≤0.25 - 256| 297| Bacteroides fragilis (ATCC 23745)| 0.06 - ?| 334| Bacteroides fragilis (ATCC 25285)| 1 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis (BF-1363 + clindamycin-resistant)| >128 - ?| 248| Bacteroides fragilis (GAI 0558)| 0.5 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis (GAI 5562)| 0.5 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis (GAI 7955)| 1 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| <=0.25 - >=512| 1453| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| 0.01 - >=256| 1480| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| <0.125 - >128| 1399| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| <=0.016 - >32| 1466| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| <=0.016 - >32| 1469| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| <=0.06 - >256| 1468| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| 0.008 - >64| 1473| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| 0.06 - >128| 1475| Bacteroides fragilis (Imipenem-resistant)| 1 - >128| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis (NCTC 10581)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides fragilis (NCTC 9343)| 0.5 - ?| 401| Bacteroides fragilis (UC12199)| 1 - ?| 240| Bacteroides fragilis gr.| ≤0.06 - >256| 497| Bacteroides melaninogenicus| ? - ?| 1385| Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. Intermedius| <=0.062 - 1| 1470| Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. Melaninogenicus| <=0.062 - 1| 1470| Bacteroides merdae| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Bacteroides merdae| ≤0.06 - >256| 497| Bacteroides oralis| <=0.062 - 0.25| 1470| Bacteroides ovatus| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Bacteroides ovatus| 2 - >16| 1474| Bacteroides ovatus| 1 - >32| 1466| Bacteroides ovatus| ? - ?| 1385| Bacteroides ovatus| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides ovatus| ≤0.06 - >256| 497| Bacteroides ovatus| 2 - >32| 1469| Bacteroides ovatus| 2 - >64| 1473| Bacteroides ovatus (ATCC 8483)| 0.5 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides pneumosintes| 0.125 - ?| 1470| Bacteroides putredinis| <=0.062 - ?| 1470| Bacteroides ruminicola| 0.125 - ?| 1470| Bacteroides ruminicola subsp. brevis| <0.062 - 4| 1470| Bacteroides stercoris| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides tectum| <=0.015 - 0.125| 1460| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 0.03 - >128| 248| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| <=0.062 - 8| 1470| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| ? - ?| 1385| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| ≤0.06 - >256| 497| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 0.25 - >16| 1474| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 0.25 - >32| 1466| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 0.5 - >32| 1469| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 0.1 - >256| 1468| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 1 - >128| 1477| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 0.5 - >128| 1475| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (ATCC 29741)| 4 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (Imipenem-resistant)| 1 - >128| 1477| Bacteroides uniformis| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides uniformis| 0.03 - 4| 1473| Bacteroides uniformis| ≤0.06 - >256| 497| Bacteroides uniformis| 0.5 - >128| 1475| Bacteroides uniformis| <=0.06 - >256| 1468| Bacteroides uniformis| 0.5 - 4| 1466| Bacteroides uniformis (ATCC 8492)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides ureolyticus| ≤0.03 - 2| 818| Bacteroides ureolyticus| 0.03 - 0.5| 1460| Bacteroides ureolyticus (NCTC 10941)| 0.25 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides vulgatus| <=0.016 - >16| 1474| Bacteroides vulgatus| <=0.016 - >32| 1466| Bacteroides vulgatus| <=0.016 - >32| 1469| Bacteroides vulgatus| 0.03 - >128| 248| Bacteroides vulgatus| <0.008 - >64| 1473| Bacteroides vulgatus| <=0.06 - >256| 1468| Bacteroides vulgatus| ? - ?| 1385| Bacteroides vulgatus| ≤0.06 - >256| 497| Bacteroides vulgatus| 0.06 - >128| 1475| Bacteroides vulgatus| <=0.5 - >128| 1476| Bacteroides vulgatus| 0.06 - >128| 982| Bacteroides vulgatus| <=0.062 - ?| 1470| Bacteroides vulgatus (ATCC 8482)| 0.06 - ?| 1477| Bacteroides xylanisolvens| 0.5 - ?| 1454| Bifidobacterium adolescentis| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Bifidobacterium adolescentis (ATCC 15703)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Bifidobacterium bifidum (JCM 1255)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Bifidobacterium breve| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Bifidobacterium breve| 1 - ?| 1470| Bifidobacterium breve (ATCC 15700)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Bifidobacterium longum| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Bifidobacterium longum (ATCC 15707)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Bifidobacterium pseudolongum (ATCC 25526)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Bifidobacterium sp.| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Bifidobacterium spp.| ≤0.004 - 0.06| 340| Bifidobacterium spp.| <=0.016 - >32| 1466| Bifidobacterium spp.| 0.03 - 8| 1469| Bifidobacterium spp.| 0.03 - 1| 1473| Bilophila wadsworthia| 0.25 - 2| 1460| Bilophila wadsworthia (WAL 7959)| 0.5 - ?| 1477| Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (2000-2004 + Spain)| 0.5 - >4| 603| Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (2006-2007 + Spain)| 0.5 - >4| 603| Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (ATCC 27164)| 0.06 - 0.125| 603| Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (ATCC 27164)| 0.063 - ?| 603| Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (ATCC 27164)| ≤0.125 - ?| 603| Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (ATCC 31212)| 1 - >4| 603| Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (ATCC 31212)| >4 - ?| 603| Brevibacterium spp.| 0.5 - >64| 185| Callyspongia fallax| 0.02 - 8| 29| Campylobacter coli| 0.25 - >32| 833| Campylobacter concisus| 0.125 - 4| 818| Campylobacter gracilis| 0.125 - 4| 818| Campylobacter gracilis (JCM 8538)| 0.125 - ?| 1477| Campylobacter jejuni| 0.12 - 8| 833| Campylobacter jejuni| 0.125 - 2| 982| Campylobacter mucosalis| 0.125 - 4| 818| Campylobacter rectus| 0.125 - 4| 818| Campylobacter showae| 0.125 - 4| 818| Campylobacter sputorum| 0.125 - 4| 818| Capnocytophaga ochracea| ≤0.03 - 2| 818| Capnocytophaga ochracea (GAI 5586)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Capnocytophaga spp.| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Capnocytophaga spp.| <1 - ?| 821| Cellulomonas biazotea| 2 - ?| 827| Cellulomonas cellasea| 0.06 - ?| 827| Cellulomonas fermentans| 0.25 - ?| 827| Cellulomonas fimi| 2 - ?| 827| Cellulomonas flavigena| 0.5 - ?| 827| Cellulomonas gelida| 1 - ?| 827| Cellulomonas hominis (CDC A-3 + CE39)| 8 - ?| 827| Cellulomonas hominis (CDC A-3 + CE40)| 8 - ?| 827| Cellulomonas uda| 2 - ?| 827| Clostridium baratii| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium bifermentans| 0.02 - 8| 29| Clostridium bifermentans| ? - ?| 1385| Clostridium bifermentans| 0.03 - 8| 1466| Clostridium bifermentans| 0.016 - >64| 1473| Clostridium bifermentans| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium bifermentans| 0.06 - 0.25| 1474| Clostridium bifermentans (NCTC 06800)| 1 - ?| 1477| Clostridium butyricum| 0.02 - 8| 29| Clostridium butyricum| <=0.03 - 4| 1475| Clostridium cadaveris| 0.02 - 8| 29| Clostridium cadaveris| 0.03 - 8| 1466| Clostridium cadaveris| 0.016 - >64| 1473| Clostridium cadaveris| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium cadaveris| 0.03 - ?| 1474| Clostridium cadaveris| 0.5 - ?| 1470| Clostridium clostridioforme| <=0.015 - 2| 1460| Clostridium clostridioforme| 0.02 - 2| 29| Clostridium clostridioforme| <=0.03 - 4| 1475| Clostridium clostridioforme| 0.06 - ?| 1474| Clostridium clostridioforme (NCTC 11224)| 0.25 - ?| 1477| Clostridium cochlearium| 0.02 - 8| 29| Clostridium difficile| 0.25 - >32| 1460| Clostridium difficile| ? - ?| 1385| Clostridium difficile| 1 - >32| 1279| Clostridium difficile| ? - ?| 381| Clostridium difficile| 1 - >=32| 241| Clostridium difficile| 2 - >32| 1469| Clostridium difficile| 2 - >32| 1466| Clostridium difficile| 4 - >16| 1474| Clostridium difficile| 8 - >16| 462| Clostridium difficile| 2 - >32| 29| Clostridium difficile| 4 - >64| 1473| Clostridium difficile| 4 - >128| 1477| Clostridium difficile| 4 - 128| 1470| Clostridium difficile| 0.25 - 128| 1476| Clostridium difficile| 6 - ?| 248| Clostridium difficile| 8 - ?| 1474| Clostridium difficile (GAI 10029)| >128 - ?| 1477| Clostridium glycolicum| 0.02 - 8| 29| Clostridium hastiforme| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium histolyticum| 0.03 - 8| 1466| Clostridium innocuum| 0.25 - 32| 29| Clostridium innocuum| 0.25 - >32| 1460| Clostridium innocuum| 0.5 - 2| 1474| Clostridium innocuum| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium innocuum| 0.5 - 1| 1476| Clostridium novyi (A)| 0.02 - 8| 29| Clostridium oroticum| 0.02 - 8| 29| Clostridium paraputrificum| 0.02 - 8| 29| Clostridium paraputrificum| 0.03 - 8| 1466| Clostridium paraputrificum| 8 - ?| 1474| Clostridium paraputrificum (ATCC 25780)| 8 - ?| 1477| Clostridium perfringens| 0.008 - 4| 340| Clostridium perfringens| <=0.016 - 2| 1466| Clostridium perfringens| 0.06 - >32| 241| Clostridium perfringens| ? - ?| 1385| Clostridium perfringens| 0.06 - 1| 29| Clostridium perfringens| 0.06 - 2| 1475| Clostridium perfringens| 0.06 - 4| 1474| Clostridium perfringens| 0.125 - 2| 1476| Clostridium perfringens| 0.06 - 4| 1473| Clostridium perfringens| <=0.03 - >128| 1477| Clostridium perfringens| 0.06 - 4| 1467| Clostridium perfringens| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium perfringens| 0.125 - >32| 29| Clostridium perfringens| 0.06 - 2| 982| Clostridium perfringens| <=0.062 - 0.125| 1470| Clostridium perfringens| 0.125 - 2| 1474| Clostridium perfringens| 0.25 - ?| 298| Clostridium perfringens| 0.25 - ?| 1333| Clostridium perfringens| 4.003 - ?| 248| Clostridium perfringens (ATCC 13124)| 0.06 - ?| 1477| Clostridium putrificum (ATCC 25784)| 32 - ?| 1477| Clostridium ramosum| <=0.03 - 4| 1475| Clostridium ramosum| ? - ?| 1385| Clostridium ramosum| 0.25 - 4| 1460| Clostridium ramosum| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium ramosum| 0.5 - ?| 1470| Clostridium ramosum| 6 - ?| 248| Clostridium ramosum (ATCC 25582)| 8 - ?| 1477| Clostridium septicum| <=0.03 - 4| 1475| Clostridium septicum (ATCC 12464)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Clostridium sordellii| 0.03 - 8| 1466| Clostridium sordellii| 0.016 - >64| 1473| Clostridium sordellii| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium sordellii| 1 - ?| 1474| Clostridium sordellii (NCTC 06929)| 1 - ?| 1477| Clostridium sordellii (NCTC 08780)| 1 - ?| 1477| Clostridium species (NOS)| ? - ?| 1385| Clostridium sporogenes| <=0.03 - 4| 1475| Clostridium sporogenes| ? - ?| 1385| Clostridium spp.| <=0.03 - 32| 1477| Clostridium spp.| 0.008 - >128| 341| Clostridium spp.| 0.06 - 8| 241| Clostridium spp.| 0.03 - 8| 1466| Clostridium spp.| 0.06 - >32| 241| Clostridium spp.| 0.016 - >64| 1473| Clostridium spp.| <0.03 - 4| 982| Clostridium tertium| 0.03 - 8| 1466| Clostridium tertium| 0.016 - >64| 1473| Clostridium tertium| 0.06 - >32| 1469| Clostridium tertium| 1 - >32| 241| Collinsella aerofaciens| ≤0.03 - 0.25| 818| Corynebacterium (CDC group G)| 0.02 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium accolens| 0.02 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium amycolatum| 0.125 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium amycolatum| 0.5 - >64| 185| Corynebacterium aquaticum| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Corynebacterium aquaticum| 0.02 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium falsenii| 0.02 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium jeikeium| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Corynebacterium jeikeium| 1 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium jeikeium| 0.5 - >64| 185| Corynebacterium minutissimum| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Corynebacterium minutissimum| 0.02 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium minutissimum| ≤0.03 - >64| 185| Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum| 0.02 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium spp.| >8 - ?| 123| Corynebacterium spp.| 0.03 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium spp.| 0.12 - >128| 15| Corynebacterium spp. (group 2)| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Corynebacterium spp. (group ANF-1)| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Corynebacterium spp. (group ANF-3)| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Corynebacterium striatum| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Corynebacterium striatum| 0.02 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium striatum| >64 - ?| 185| Corynebacterium urealyticum| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Corynebacterium urealyticum| 0.02 - >32| 29| Corynebacterium urealyticum| 1 - >64| 185| Corynebacterium urealyticum (with no species identified)| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Dermabacter hominis| 0.02 - >32| 29| Desulfovibrio piger (DSM 749)| 0.06 - ?| 1477| Dialister pneumosintes| ≤0.03 - 2| 818| Edwardsiella hoshinae| 4 - 64| 1409| Edwardsiella ictaluri| 1 - 32| 1409| Edwardsiella tarda| 4 - 64| 1409| Eggerthella lenta| 0.125 - 1| 241| Eggerthella lenta (ATCC 25559)| 0.25 - ?| 1477| Eggerthella lenta (ATCC 43055)| 0.125 - ?| 1477| Eikenella corrodens| 8 - >32| 818| Eikenella corrodens| >64 - ?| 821| Enterococcus| ≤0.125 - 32| 1036| Enterococcus avium| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus casseliflavus| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus cecorum| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus durans| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus faecalis| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Enterococcus faecalis| 8 - >8| 123| Enterococcus faecalis| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus faecalis| 4 - ?| 1165| Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212)| 8 - ?| 401| Enterococcus faecalis (erythromycin-resistant + vancomycin-susceptible)| 16 - >256| 448| Enterococcus faecalis (erythromycin-susceptible + vancomycin-susceptible)| 16 - 32| 448| Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-resistant)| >16 - ?| 496| Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-resistant)| >256 - ?| 448| Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible)| 16 - >16| 496| Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible)| 16 - >256| 448| Enterococcus faecium| 0.12 - >8| 123| Enterococcus faecium (12311 + vancomycin-resistant)| >128 - ?| 286| Enterococcus faecium (12366 + vancomycin-resistant)| >128 - ?| 286| Enterococcus faecium (ACA-DC 3350)| ≤1 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (ACA-DC 3359)| ≤1 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (erythromycin-resistant + vancomycin-resistant)| 0.06 - >256| 448| Enterococcus faecium (erythromycin-resistant + vancomycin-susceptible)| 0.12 - >256| 448| Enterococcus faecium (erythromycin-susceptible + vancomycin-susceptible)| 0.12 - 16| 448| Enterococcus faecium (PCD 71)| 4 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (PCK 38)| 2 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (PCK 45)| ≤1 - ?| 910| Enterococcus faecium (vancomycin-resistant)| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus faecium (vancomycin-resistant)| ≤0.25 - >16| 496| Enterococcus faecium (vancomycin-resistant)| ? - ?| 602| Enterococcus faecium (vancomycin-susceptible)| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus faecium (vancomycin-susceptible)| ≤0.25 - >16| 496| Enterococcus faecium (vancomycin-susceptible)| 0.12 - >256| 448| Enterococcus faecium (vancomycin-susceptible)| ? - ?| 602| Enterococcus gallinarum| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus raffinosus| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Enterococcus spp.| 0.12 - >8| 123| Enterococcus spp.| 8 - >16| 496| Enterococcus spp. (macrolide-resistant)| >128 - ?| 15| Enterococcus spp. (macrolide-susceptible)| 0.25 - 32| 15| Escherichia coli| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Escherichia coli| 64 - ?| 961| Escherichia coli| 64 - ?| 982| Escherichia coli (HB103::pBglII)| ≥128 - ?| 729| Escherichia coli (HB103::pBluescript)| 32 - ?| 729| Eubacterium brachy| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium combesii| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium contortum| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium lentum| ≤0.03 - 0.25| 818| Eubacterium lentum| 0.03 - 1| 1473| Eubacterium lentum| 0.5 - 1| 1476| Eubacterium lentum| 1 - ?| 1470| Eubacterium lentum (ATCC 43055)| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium limosum| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium saburreum| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium saburreum| ≤0.03 - 0.25| 818| Eubacterium spp.| <0.004 - 0.25| 341| Eubacterium spp.| <=0.062 - 1| 1470| Eubacterium spp.| 0.03 - 8| 1469| Eubacterium spp.| ≤0.03 - 0.25| 818| Eubacterium spp.| 0.06 - 0.25| 1466| Eubacterium tenue| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium timidum| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium timidum| ≤0.03 - 0.25| 818| Eubacterium yurii| 0.02 - 1| 29| Eubacterium yurii| ≤0.03 - 0.25| 818| Finegoldia magna| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Finegoldia magna| 0.02 - 1| 29| Finegoldia magna| 0.125 - >32| 241| Finegoldia magna| 0.125 - >256| 1452| Finegoldia magna| 0.125 - >16| 1474| Finegoldia magna| 0.25 - 4| 1474| Finegoldia magna (ATCC 29328)| 2 - ?| 1477| Finegoldia magna (Levofloxacin-resistant)| <=0.03 - >128| 1477| Fusobacteria| 0.03 - 32| 1469| Fusobacteria| 0.016 - 64| 1473| Fusobacterium (penicillin-susceptible)| 0.03 - 0.25| 1396| Fusobacterium (penicillin-susceptible)| 0.06 - 0.12| 1396| Fusobacterium gonidiaformans| <=0.015 - 2| 1460| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.06 - 0.25| 1466| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.06 - 8| 1474| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.06 - 0.125| 1469| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.125 - 4| 1473| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.06 - 8| 1460| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.25 - >128| 1475| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.125 - ?| 1470| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 18 - ?| 248| Fusobacterium naviforme| ≤0.03 - 0.06| 818| Fusobacterium naviforme| <=0.015 - 2| 1460| Fusobacterium necrogenes| 0.06 - 8| 1460| Fusobacterium necrophorum| ≤0.03 - 0.06| 818| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.016 - 0.05| 1473| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.03 - 0.06| 1469| Fusobacterium necrophorum| <=0.015 - 2| 1460| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.03 - 0.125| 1474| Fusobacterium necrophorum| <=0.03 - 32| 1477| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.25 - >128| 1475| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.02 - 3.1| 1444| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.03 - ?| 1466| Fusobacterium necrophorum| <=0.063 - ?| 1470| Fusobacterium necrophorum (ATCC 25286)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Fusobacterium nucleatum| ? - ?| 381| Fusobacterium nucleatum| ≤0.03 - <=0.03| 818| Fusobacterium nucleatum| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Fusobacterium nucleatum| 0.06 - 0.125| 1466| Fusobacterium nucleatum| <=0.015 - 2| 1460| Fusobacterium nucleatum| 0.03 - 0.125| 1469| Fusobacterium nucleatum| 0.03 - 0.125| 1474| Fusobacterium nucleatum| 0.06 - 0.125| 1473| Fusobacterium nucleatum| <=0.03 - 32| 1477| Fusobacterium nucleatum| 0.25 - >128| 1475| Fusobacterium nucleatum| 0.06 - 0.125| 1474| Fusobacterium nucleatum| <=0.062 - 0.25| 1470| Fusobacterium nucleatum| <1 - ?| 821| Fusobacterium nucleatum (ATCC 25586)| 0.06 - ?| 1477| Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. animalis| <=0.015 - 2| 1460| Fusobacterium russii| <=0.015 - 0.125| 1460| Fusobacterium spp.| 0.015 - >128| 340| Fusobacterium spp.| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Fusobacterium spp.| 0.06 - 8| 1467| Fusobacterium spp.| <=0.03 - 32| 1477| Fusobacterium spp.| 0.03 - >32| 1466| Fusobacterium spp.| 0.25 - >128| 1475| Fusobacterium spp.| 0.25 - >128| 982| Fusobacterium ulcerans| 0.06 - 8| 1460| Fusobacterium varium| 0.06 - 16| 1460| Fusobacterium varium| 2 - >16| 1474| Fusobacterium varium| 0.25 - >128| 1475| Fusobacterium varium| 1 - >32| 1466| Fusobacterium varium| 2 - 32| 1469| Fusobacterium varium| 2 - 64| 1473| Fusobacterium varium| <=0.062 - 32| 1470| Fusobacterium varium| 18 - ?| 248| Fusobacterium varium (ATCC 8501)| 4 - ?| 1477| Gardnerella vaginalis| ≤0.03 - 0.25| 305| Gardnerella vaginalis (ATCC 14018)| ≤0.03 - ?| 305| Gemella morbillorum| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Gemella morbillorum (ATCC 27824)| 0.06 - ?| 1477| Gemella spp.| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Haemophilus influenzae| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Haemophilus influenzae| 0.5 - 16| 982| Haemophilus influenzae| 0.5 - 16| 961| Haemophilus influenzae (ESBL)| 1 - >4| 84| Haemophilus influenzae (ESBL)| 2 - >4| 84| Haemophilus influenzae (ESBL)| 2 - >4| 114| Haemophilus influenzae (non-ESBL)| 1 - >4| 114| Haemophilus parahaemolyticus| ? - ?| 307| Haemophilus parainfluenzae| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Haemophilus parasuis (Spain)| 0.25 - 4| 768| Haemophilus parasuis (UK)| 0.25 - 4| 768| Helicobacter pylori| 0.1 - 50| 662| Hemolytic streptococci (group C)| 0.064 - >256| 1544| Hemolytic streptococci (group G)| 0.064 - >256| 1544| Jonesia denitrificans| 8 - ?| 827| Klebsiella pneumonia| 125 - ?| 961| Klebsiella pneumonia| 125 - ?| 982| Klebsiella pneumoniae| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Lactobacillus acidophilus| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus acidophilus| ≤0.125 - 0.25| 1036| Lactobacillus acidophilus| 0.5 - 16| 878| Lactobacillus acidophilus (CRL 1251)| 0.1 - ?| 1268| Lactobacillus acidophilus (CRL 1266)| 10 - ?| 1268| Lactobacillus acidophilus (Etest)| ≤0.12 - >=256| 1036| Lactobacillus acidophilus (JCM 1132)| 1 - ?| 1477| Lactobacillus amylovorus (Etest)| ≤0.12 - >=256| 1036| Lactobacillus brevis| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus brevis| 4 - 32| 878| Lactobacillus brevis (JCM 1059)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Lactobacillus buchneri| ≤0.125 - 1| 1036| Lactobacillus casei| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus casei| 0.5 - 32| 878| Lactobacillus casei (JCM 1134)| 2 - ?| 1477| Lactobacillus catenaforme| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Lactobacillus catenaforme| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus crispatus (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 2| 1036| Lactobacillus curvatus| 8 - 64| 878| Lactobacillus delbrueckii| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Lactobacillus delbrueckii| 0.25 - 64| 878| Lactobacillus delbrueckii (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 2| 1036| Lactobacillus fermentans| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus fermentum| 1 - 64| 878| Lactobacillus fermentum (Etest)| ≤0.12 - ?| 1036| Lactobacillus fermentum (JCM 1173)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Lactobacillus gallinarum (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 1| 1036| Lactobacillus gasseri (CRL 1259)| 1 - ?| 1268| Lactobacillus gasseri (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 16| 1036| Lactobacillus helveticus (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 4| 1036| Lactobacillus jensenii| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus johnsonii (CRL 1294)| >100 - ?| 1268| Lactobacillus johnsonii (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 16| 1036| Lactobacillus minutus| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus oris| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Lactobacillus oris| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus paracasei (CRL 1289)| >100 - ?| 1268| Lactobacillus paracasei (Etest)| ≤0.25 - 4| 1036| Lactobacillus paracasei (MDIL)| ≤0.25 - 16| 1036| Lactobacillus pentosus (PCD 101)| 4 - ?| 910| Lactobacillus plantarum| ≤3 - >32| 818| Lactobacillus plantarum| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus plantarum| ≤0.125 - >=256| 1036| Lactobacillus plantarum| 0.5 - 128| 878| Lactobacillus plantarum (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 8| 1036| Lactobacillus plantarum (JCM 1149)| 0.25 - ?| 1477| Lactobacillus plantarum (MDIL)| ≤0.12 - 8| 1036| Lactobacillus reuteri| ≤0.125 - 0.25| 1036| Lactobacillus reuteri (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 2| 1036| Lactobacillus reuteri (JCM 1112)| <=0.03 - ?| 1477| Lactobacillus reuteri (MDIL)| ≤0.12 - 16| 1036| Lactobacillus rhamnosus| 0.02 - >32| 29| Lactobacillus rhamnosus| ≤0.125 - 0.5| 1036| Lactobacillus rhamnosus| 0.5 - 32| 878| Lactobacillus rhamnosus (Agar dilution)| ≤0.125 - 8| 1036| Lactobacillus rhamnosus (Broth microdilution)| ≤0.125 - 8| 1036| Lactobacillus rhamnosus (Etest)| ≤0.12 - 16| 1036| Lactobacillus rhamnosus (Etest)| ≤0.125 - 16| 1036| Lactobacillus rhamnosus (MDIL)| ≤0.12 - 8| 1036| Lactobacillus sakei| 8 - 64| 878| Lactobacillus sakei (MDIL)| ≤0.12 - 16| 1036| Lactobacillus salivarius| ≤0.125 - 0.5| 1036| Lactobacillus salivarius (CRL 1328)| 0.1 - ?| 1268| Lactobacillus salivarius (JCM 1231)| 0.06 - ?| 1477| Lactobacillus sp.| 0.25 - 128| 878| Lactobacillus sp.| 8 - ?| 1470| Lactobacillus spp.| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Lactobacillus spp.| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Lactobacillus spp.| 0.015 - 128| 340| Lactobacillus spp.| 0.03 - 1| 1473| Lactobacillus spp.| 0.25 - 4| 1466| Lactobacillus spp.| 0.03 - 0.12| 448| Lactobacillus spp.| 0.5 - 1| 1476| Lactobacillus spp.| 8 - ?| 1401| Lactococcus| ≤0.125 - 32| 1036| Leptotrichia buccalis| ≤0.03 - 0.06| 818| Leptotrichia buccalis| 0.125 - ?| 1470| Leuconostoc| ≤0.125 - 32| 1036| Leuconostoc mesenteroides (PCD 119)| 4 - ?| 910| Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides (PCK 18)| ≤1 - ?| 910| Leuconostoc spp.| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Leuconostoc spp.| 0.015 - 0.06| 448| Leuconostoc spp.| <500 - ?| 1096| Listeria monocytogenes| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Listeria monocytogenes| 0.25 - 2| 185| Micrococcus spp.| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Micromonas micros| ≤0.03 - 0.25| 818| Micromonas micros| 0.125 - 1| 241| Micromonas micros| 0.125 - 0.5| 1474| Micromonas micros| 0.125 - 16| 1477| Micromonas micros (VPI 5464-1)| 0.25 - ?| 1477| Moraxella catarrhalis| >2 - ?| 462| Moraxella catarrhalis| 1 - >4| 84| Moraxella catarrhalis| 1 - >4| 114| Moraxella catarrhalis| 0.016 - >256| 1544| Mycobacterium smegmatis| 8 - ?| 614| Mycobacterium smegmatis (A-2572U)| 16 - ?| 614| Mycobacterium smegmatis (C2055A)| 16 - ?| 614| Mycobacterium smegmatis (U2504G)| 16 - ?| 614| Mycoplasma fermentans| ≤0.008 - 0.031| 139| Mycoplasma fermentans| ≤0.008 - 0.063| 182| Mycoplasma hominis| ≤0.008 - 0.125| 182| Mycoplasma hominis| ≤0.008 - 0.125| 139| Mycoplasma hominis| <2 - ?| 1006| Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (F18)| 0.125 - 0.25| 761| Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (F19)| >64 - ?| 761| Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (F2)| 0.0625 - ?| 761| Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (F5)| 0.125 - 0.25| 761| Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (F6)| 0.125 - ?| 761| Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (J-strain)| 0.5 - ?| 761| Mycoplasma hyosynoviae| <=0.12 - 0.25| 1513| Mycoplasma pneumonia| ? - ?| 602| Neisseria cinerea| 16 - >256| 1544| Neisseria elongata| 16 - >256| 1544| Neisseria gonorrhoeae| 0.5 - 4| 961| Neisseria meningitidis| 4 - ?| 961| Neisseria meningitidis| 4 - ?| 982| Neisseria sicca| 16 - >256| 1544| Neisseria spp.| 16 - >256| 1544| Nocardia asteroides| 100 - >=400| 1404| Oerskovia turbata| 4 - ?| 827| Oerskovia xanthineolytica| 4 - ?| 827| Olsenella uli| ≤0.03 - >32| 818| Parvimonas micra| 0.047 - 2| 1452| Pediococcus| ≤0.125 - 32| 1036| Pediococcus pentosaceus (PCD 215)| ≤1 - ?| 910| Pediococcus pentosaceus (PCD 237)| 16 - ?| 910| Pediococcus spp.| ≤0.12 - >16| 18| Pediococcus spp.| 0.03 - 0.25| 448| Peptococcus asaccharolyticus| ? - ?| 1385| Peptococcus asaccharolyticus| <=0.062 - 1| 1470| Peptococcus magnus| <=0.062 - 2| 1470| Peptococcus prevotii| 0.02 - 1| 29| Peptococcus spp.| 0.015 - >128| 248| Peptoniphilus asaccharolyticus| 0.06 - >16| 1474| Peptoniphilus asaccharolyticus (Levofloxacin-resistant)| <=0.03 - >128| 1477| Peptoniphilus asaccharolyticus (WAL 3218)| >128 - ?| 1477| Peptoniphilus gorbachii| 0.125 - 0.75| 1452| Peptoniphilus harei| 0.094 - 1.5| 1452| Peptoniphilus indolicus (GAI 0915)| 32 - ?| 1477| Pepton
|