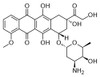
Doxorubicin HCl is an anthracycline antibiotic and 12-hydroxylated version of daunorubicin that inhibits macromolecular biosynthesis through DNA intercalation.
| Mechanism of Action | Doxorubicin stops the development of the topoisomerase II enzyme, which relaxes supercoils in DNA for transcription. Doxorubicin stabilizes the topoisomerase II complex after it has broken the DNA chain for replication, which prevents the DNA double helix from being resealed and thereby inhibits the replication process. |
| Impurity Profile | Impurity A| (8S,10S)-8-acetyl-10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione (daunorubicin)|||| Impurity B| (8S,10S)-10[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-8-(2-bromo-1,1-dimethoxyethyl)-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione|||| Impurity C| (8S,10S)-10[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-8-(bromoacetyl)-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione|||| Impurity D| (8S,10S)-6,8,10,11-tetrahydroxy-8-(hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione (doxorubicin aglycone, doxorubicinone)| |
| Cancer Applications | Doxorubicin is given to treat non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, multiple myeloma, acute leukemias, Kaposi sarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, Wilm tumor, and cancers of the breast, adrenal cortex, endometrium, lung, ovary, and other sites. It is sometimes used to treat non-cancerous conditions as well. |