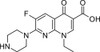
Enoxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic with a broad spectrum (Gram-positive and Gram-Negative) of activity. Enoxacin was used to treat urinary tract infections and gonorrhea.
| Mechanism of Action | Fluoroquinolone antibiotics target bacterial DNA gyrase, an enzyme which reduces DNA strain during replication. Because DNA gyrase is required during DNA replication, subsequent DNA synthesis and cell division is inhibited. |
| Spectrum | Enoxacin has a broad spectrum of activity and is active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. |
| Molecular Formula | C15H17FN4O3 ● 1.5H2O |