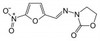
Furazolidone is a synthetic nitrofuran antibiotic and monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) with antiprotozoal and antibacterial activity. It is effective against a range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is often used to treat gastrointestinal infections.
| Mechanism of Action | Furazolidone targets bacterial DNA to induce crosslinks which lead to an increased mutation rate or prevents complete DNA replication. |
| Spectrum | Furazolidone is a broad-spectrum antibiotic targeting bacteria responsible for gastrointestinal infections. |
| Microbiology Applications | Furazolidone is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options for infected patients. Representative MIC values include:
|
| Molecular Formula | C8H7N3O5 |
| References |
Chatterjee SN (1979) Mechanism of action of Furazolidone: Inter-strand cross-linking in DNA & liquid holding recovery of Vibrio Cholerae Cells." Indian J. Biochem. and Biophys. 16 (3):125-30 |
| MIC | Lactobacillus reuteri| 90|| Treponema hyodysenteriae | ≤0.1 - 1.56 || Vibrio harveyi| 12.5|| |