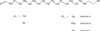Gramicidin is a combination of six different antimicrobial polypeptides. Gramicidin is insoluble in aqueous solution.
| Mechanism of Action | Gramicidin targets and inserts into the gram positive membrane where it disrupts normal permeability leading to cell death. Gramicidin is typically used as a topical antimicrobial agent because it also causes hemolysis of red blood cells |
| Spectrum | Gramicidin targets primarily the cell membrane of Gram positive bacteria and shows little effect against Gram negative bacteria. |
| Molecular Formula | Gramicidin A1: C99H140N20O17 |
| Solubility | Acetic acid: Soluble Lower alcohols: Soluble Water: Almost insoluble |
| Elemental Analysis | Composition: Gramicidin A1, A2, B1, C1 and C2: ≥95.0% Gramicidin A1: ≥60.0% |
| References | Farmer, S. W., and et al. "Gramicidin S Is Active against Both Gram-positive and Gram-negative Bacteria." International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research 47.6 (1996): 460-66. www.ncbi.gov. Web. 4 Sept. 2012. |
| MIC | Listeria innocua| 0.25|| Listeria monocytogenes| 0.5|| |