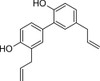
Honokiol is a bioactive component of Magnolia obovata, known for its medicinal properties in traditional Asian medicine. Researchers have been interested in its promising antitumor activity, and have reported honokiol inducing apoptosis and inhibiting angiogenesis in a variety of cancers including colon and breast cancer.
Honokiol has also demonstrated antibiofilm activity in Candida albicans, inhibiting the adhesion of planktonic fungal cells to a surface to begin biofilm formation.
Honokiol is soluble in organic solvents.
| References | Fried, L. E., & Arbiser, J. L. (2009). Honokiol, a Multifunctional Antiangiogenic and Antitumor Agent. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 11(5), 1139-1148. doi:10.1089/ars.2009.2440 Sun, L., Liao, K., & Wang, D. (2015). Effects of Magnolol and Honokiol on Adhesion, Yeast-Hyphal Transition, and Formation of Biofilm by Candida albicans. PLOS ONE PLoS ONE, 10(2). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0117695 |