Hygromycin B is a unique aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Hygromycin B is routinely used as a selective agent in cell culture or microbiology applications to isolate Hygromycin B resistant cells.
This product is packaged as a concentrated solution containing 350-450 units/mL.
This product is considered a dangerous good. Quantities above 1 g may be subject to additional shipping fees. Please contact us for specific questions.
For more Hygromycin B products, click here.
| Mechanism of Action | Hygromycin B inhibits protein synthesis by strengthening the interaction of tRNA binding in the ribosomal A-site. Hygromycin B also prevents mRNA and tRNA translocation by an unknown mechanism. These are unique mechanisms for an aminoglycoside antibiotic and they differ from the mode of action neomycin, gentamicin, and G418. |
| Spectrum | Hygromycin B is effective against eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. |
| Microbiology Applications | Hygromycin B can be used as a selection agent to isolate hygromycin b resistant bacteria and fungi. |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | Hygromycin B is routinely used as a selective agent in mammalian cell culture to isolate hygromycin B resistant cells after transfection. Selectable markers for hygromycin B resistant cells include the hyg or hph resistance genes which express a phosphotransferase that inactivates hygromycin B by phosphorylation. Effective working concentrations range from 100 – 1000 µg/mL.
For additional information regarding relevant cell lines, resistance plasmids, and culture media, please visit our cell culture database. |
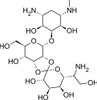
| Molecular Formula |
C20H37N3O13 |
| Source |
Biosynthetic: produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. |
| Documents | Hygromycin Protocol.pdfPlasmid_DNA_Transfection_Protocol.pdf|Selection_of_Stable_Transfected_Cell_Lines_Protocol.pdf |
| References |
Dai S., Zheng P., Marmey P., Zhang S., Tian W., Chen S., Beachy R.N. and Fauquet C. Comparative analysis of transgenic rice plants obtained by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and particle bombardment. Molecular Breeding 7: 25–33, 2001. © 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Schindler, D. "Studies on the Mode of Action of Hygromycin B, an Inhibitor of Translocation in Eukaryotes." Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 521.2 (1978): 459-69. www.ncbi.gov. Web. 6 Sept. 2012. |
| Protocols |
Hygromycin B Kill Curve ProtocolBackground: Hygromycin B is a unique aminoglycoside antibiotic produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus and is routinely used as a selective agent in cell culture and microbiology applications to isolate transfected, hygromycin B resistant cells. Before stable transfected cell lines can be selected, the optimal hygromycin B concentration needs to be determined by performing a kill curve titration. The optimal working concentration of hygromycin B suitable for selection of resistant mammalian clones depends on the cell lines, media, growth conditions, and the quality of hygromycin B. Because of these variables, it is necessary to perform a kill curve for every new cell type and new batch of hygromycin B. Preparation and storage of hygromycin B solution: Hygromycin B is soluble in water at >50 mg/mL. It is also soluble in methanol or ethanol. Solutions should be sterilized by filtration, not by autoclaving. Hygromycin B solutions have been reported to lose activity on freezing. Since solutions are stable refrigerated, freezing should be avoided. Hygromycin B products should be stored as supplied at 2-8 °C. The dry solid is stable for at least five years if stored at 2-8 °C. Hygromycin B solutions are stable as supplied for two years if stored at 2-8 °C. Kill Curve/Hygromycin B Titration Protocol:
Plasmid DNA Transfection Protocol
Once the appropriate antibiotic concentration to use for selection of the stable transfected cells has been determined by performing a kill curve, the next step is to generate a stable cell line by transfection of the parental cell line with a plasmid containing the gene of interest and an antibiotic resistance gene.
Plasmid DNA Transfection Protocol:
QC Seed 24-wells with insert and determine the transfection efficiency by immunostaining:
Selection of Stable Transfected Cell Lines ProtocolBackground: Once the cells have been successfully transfected, the next step is to seed and select the transfected cell line in a single 96-well plate to select pure colonies by limited dilution as outlined below:
Protocol:
QC Seed 24-wells with insert for an immunostaining to determine percentage of cells expressing the gene of interest to be able to identify a 100% pure clone. You can also use Western blotting, flow cytometry or another technique depending on the cell line used. Seed 24-wells with insert and determine the expression level of the gene of interest by immunostaining:
|