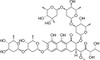
Mithramycin A was the first of the aureolic acid class of antitumor antibiotics, isolated from Streptomyces.
Mithramycin A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Limited water solubility.
Mithramycin A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Limited water solubility.
| Mechanism of Action | Mithramycin inhibits transcription and protein synthesis by non-covalent binding with G-C-rich duplex DNA in the presence of magnesium and zinc ions. Mithramycin also induces differentiation of leukemic cells accompanied by an early decrease in c-myc expression, and selectively inhibits collagen-1 gene expression in human fibroblasts. |
| References | Aureolic acid, a new antibiotic. I. Microbiological studies. Grundy W. E. et al. Antibiot. Chemother. 1953, 2, 1215. Aureolic acid group of anti-tumor antibiotics. Berlin Y. U. et al. Nature 1968, 218, 193. Mithramycin selectively inhibits the transcriptional activity of a transfected human c-myc gene Ray R. et al. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1990, 300, 203. Interaction of mithramycin with DNA. Evidence that mithramycin binds to DNA as a dimer in a right-handed screw conformation. Demicheli C. et al. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 198, 333. Mithramycin selectively inhibits collagen-alpha 1(I) gene expression in human fibroblast. Nehls M. C. et al. ; J. Clin. Invest. 1993, 92, 2916 |