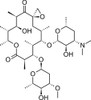
Oleandomycin is a 16-membered macrocyclic lactone, discovered in the 1950s, with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. It has activity profile similar to erythromycin and penicillin. It is synthesized from Streptomyces antibioticus. It was discovered in 1954 by Dr. Sobin and structure was determined in 1960 (Hochstein). Oleandomycin is less active than comparable products such as erythromycin. Today it is only available in combination with other antibiotics.
Oleandomycin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Limited water solubility.
| Mechanism of Action | Olendomycin is bacteriostatic, and binds to the 50s subunit of bacterial ribosomes. Unlike Erythromycin, it lacks a 12-hydroxyl group and 3-methoxy group, which changes its interactions with 50S subunit and reduces its activity. |
| Microbiology Applications | The biosynthesis mechanism and development of resistance to its antibiotic activity have been studied in order to understand the reactive enzymes in these processes. |
| References |
Els H et al (1958) Oleandomycin (PA-105). II. Chemical characterization. JACS 80:3777 Biosynthesis of Oleandomycin by Streptomyces antibioticus: Influence of nutritional conditions and development of resistance. J. Gen. Microbiol. 136(8):1447-1454 PMID 2262785 Quirós LM and SAlas JA (1995) Biosynthesis of the macrolide oleandomycin by Streptomyces antibioticus. Purification and kinetic characterization of an oleandomycin glucosyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 270(31):18234-182399 PMID 7629141 |
| Spectrum | Oleandomycin has activity against Staphylococcus and Enterococcus. |