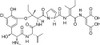
Phomopsin A is a an acidic 13-membered cyclic hexapeptide-like metabolite with three unusual amino acids linked in an ansa macrocycle with a tripeptide tail, terminating in a dicarboxylic acid. Phomopsin A is a potent mycotoxin produced by the fungus, Phomopsis leptostromiformis, and causes lupinosis in livestock fed infected lupins. Phomopsin A is an important bioprobe for understanding cellular structural proteins.
Phomopsin A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Limited water solubility.
Phomopsin A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Limited water solubility.
| Mechanism of Action | Phomopsin A binds selectively to dimeric tubulin at a site overlapping that of vinblastine and maytansine, inhibiting the formation of the microtubule spindle to block cell division. Uniquely, phomopsin A protects tubulin from decay. |
| Molecular Formula | C36H45ClN6O12 |
| References | Structure elucidation and absolute configuration of phomopsin A, a hexapeptide mycotoxin produced by phomopsis leptostromiformis. Culvenor C. C. J. et al. , Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 2351. Interaction of phomopsin A and related compounds with purified sheep brain tubulin. E. Lacey et al. , Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 2133. Interaction of phomopsin A with normal and subtilisin-treated bovine brain tubulin. Chaudhuri AR and Ludueña R.F., J. Prot. Chem. 1997, 16, 99. |