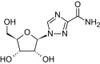
Ribavirin is an antiviral compound primarily used for hepatitis C research.
| Mechanism of Action | Ribavirn is a guanosine analog with a carboxamide group which can mimic the purine nucleosides, guanosine and adenosine. Because of its similarity to these two nucleosides, ribavirn can become incorporated into viral RNA leading to lethal mutations. |
| Spectrum | Ribavirn is active against hepatitis C and RNA viruses that cause viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs). |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N4O5 |
| References | Te S (2007) Mechanism of action of Ribavirin in the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Gastroenterol Hepatol 3(3):218-225 |