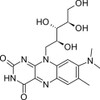
Roseoflavin is an antibacterial pigment isolated from Streptomyces davawensis as an anti-metabolite of riboflavin. Roseoflavin has been shown to be an important regulator of bacterial gene expression by binding to untranslated regions of RNA, so-called ribo-switching sites.
Roseoflavin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
Roseoflavin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Roseoflavin is used as a substrate to mimic riboflavin in flavin biosynthesis, but leading to the formation of inactive flavin co-factors. |
| Molecular Formula | C18H23N5O6 |
| References | Roseoflavin, a new antimicrobial pigment from Streptomyces. Otani S. et al. J. Antibiot. 1994, 27, 86. The bifunctional flavokinase/flavin adenine dinucleotide synthetase from Streptomyces davawensis produces inactive flavin cofactors and is not involved in resistance to the antibiotic roseoflavin. Grill S. et al. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1546. Riboswitches as antibacterial drug targets Blount K.F. & Breaker R.R.: Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1558. |