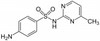
Sulfamerazine is a bacteriostatic sulfonamide antibiotic. Sulfamerazine, the monomethyl derivative of sulfadiazine, is 2-sulfanilamido-4-methylpyrimidine. It is a sulfonamide compound that inhibits bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by competing with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) for binding to dihydropteroate synthetase. Sulfamerazine can be used against the bacteria causing bronchitis, prostatitis and urinary tract infections. Solfonamides have antimicrobial and anticancer properties.
We also offer:
- Sulfamerazine (S033)
| Mechanism of Action |
Like most sulfonamides, Sulfamerazine Sodium inhibits folic acid synthesis (specifically dihydrofolic acid) by acting as a competitive inhibitor of dihydropteroate synthetase, an enzyme found in the folic acid synthesis pathway. It competes with para-amino benzoic acid for binding to the enzyme. |
| Spectrum | Sulfamerazine Sodium is a broad-spectrum antibiotic targeting a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram- negative bacteria. |
| Molecular Formula | C11H11N4O2SNa |
| References |
Aday B, Sola P, Çolak F, Kaya M (2016) Synthesis of novel sulfonamide analogs containing sulfamerazine/sulfaguanidine and their biological activities. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 31(6):1005-1010 PMID 26327456 Henry RJ (2012) The mode of action of sulfonamides. Bacteriol. Rev. (n.d.):175-84 Monti SM, Supuran CT, Simone GD (2013) Anticancer carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A patent review (2008–2013). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 23:737–749 |