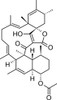
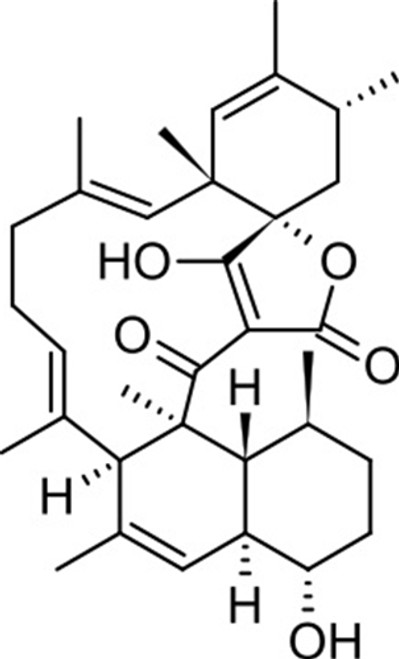
Tetromycin A is an unusual tetronic acid, structurally related to kijanimicin, chlorothricin, saccharocarcin, tetrocarcin and versipelostatin. Tetromycin A has pronounced activity against antibiotic susceptible and resistant Gram positive bacteria including MRSA. Limited availability has restricted further investigation of this metabolite in the literature. Several members of this class have received considerable literature focus. Versipelostatin inhibits transcription from the promoter of GRP78, a gene that is activated as part of a stress signalling pathway under glucose deprivation resulting in unfolded protein response (UPR). The UPR-inhibitory action is seen only in conditions of glucose deprivation and causes selective and massive killing of the glucose-deprived cells.
Tetromycin A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
Tetromycin A is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| Mechanism of Action | Tetrocarcin A appears to target the phosphatidylinositide-3'-kinase/Akt signalling pathway. |
| References | Antibiotic tetromycin A and B and its production. Takeuchi T. et al. , Japan Patent 1996, 08-165286. Effect on tumor cells of blocking survival response to glucose deprivation. Park H.R. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. et al. , 2004, 96, 1300. Apoptosis and inactivation of the PI3-kinase pathway by tetrocarcin A in breast cancers. Nakajima H. et al. , Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007, 356, 260. |