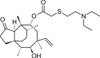
Tiamulin is a semi-synthetic analogue of pleuromutilin in which the hydroxyacetyl side chain is replaced with a larger diethylaminoethylthioacetyl moiety, providing greater hydrophobicity and an ionisable group for salt formation and greater water solubility. Tiamulin is a potent and highly selective antibiotic active against a range of Gram positive bacteria, with no cross resistance to existing antibiotic classes due to its unique mode of action. Like pleuromutilin, it inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of 23S rRNA.
Tiamulin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
Tiamulin is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF and DMSO.
| References | New pleuromutilin derivative with enhanced antimicrobial activity. I. Synthesis. Egger H. & Reinshagen H. J. Antibiot. 1976, 29, 915. Pleuromutilin antibiotics. Hunt E. Drugs Future 2000, 25, 1163. |