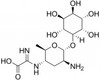
Kasugamycin Hydrochloride is a salt form a Kasugamycin, is a broad-spectrum antibacterial and antifungal aminoglycoside originally isolated in 1965 from Streptomyces kasugaensis found near the Kasuga shrine in Japan. It was discovered by Hamao Umezawa, who also discovered kanamycin and bleomycin. This natural product inhibits protein synthesis and is used against yeast and pathogenic fungi such as M. grisea. Kasugamycin is also an chitinase 1 inhibitor used in pulmonary fibrosis research.
Kasugamycin HCl is freely soluble in aqueous solution.
| Mechanism of Action |
Kasugamycin inhibits protein synthesis at the step of translation initiation by direct competition with initiator transfer RNA. It is also an CHIT1 inhibitor. |
| Plant Biology Applications |
In rice models, Kasugamycin is used to prevent and cure Magnaporthe grisea mycelia formation with <20 µg/ml. In addition, Kasugamycin has shown to suppress a number of plant parasitic infections such as leaf spot, black rot and apple scab. Kasugamycin is active against Pyricularia oryzae that causes rice blast disease, also known as rice rotten neck. Kasugamycin is active against Pseudomonas, Erwinia, Xanthomonas and Corynebacterium bacterial species. Kasugamycin HCl may be used as an analytical reference standard to determine its presence in commercial formulations. |
| Microbiology Applications |
Low level resistance to Kasugamycin is acquired via mutations in the 16S rRNA methyltransferase KsgA which methylates the nucleotides A1518 and A1519 in 16S rRNA. In a Bacillus subtilis strean harboring a single rrn operon (rrnO), authors found that spontaneous ksgA mutations confer a modest level of resistance to kasugamycin at high frequency of 10(-6). Authors found that once the cells acquired the ksgA mutations, they produce high-level kasugamycin resistance at an extraordinarily high frequency (100-fold greater frequency seen in the ksgA(+) strain) (Ochi et al, 2008). |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications |
CHIT1 (chitinase 1) contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis through the regulation of TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) signaling and effector function. Screening 7,670 small molecules through the Yale Center for Molecular Discovery, authors identified and characterized a druggable CHIT1 inhibitor in Kasugamycin with strong antifibrotic activity. In vitro studies also demonstrated that this natural copound inhibitsed fibrotic macrophage activation, fibroblast proliferation, and myofibroblast transformation. In summary, Kasugamycin demonstrated strong antifibrotic effect with potential for pulmonary fibrosis research (Lee et al, 2022). |
| Molecular Formula | C14H25N3O9 · HCl |
| References |
Lo C and Hsiao Y (1996) High-performance capillary electrophoretic method for the determination of antibiotic fungicide Kasugamycin in formulated products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 44(8):2231–2234 Lee JH et al (2022) Kasugamycin is a novel chitinase 1 inhibitor with strong antifibrotic effects on pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 67(3):309-319 PMID 35679109 Masukawa H, Tanaka N, Umezawa H (1968) Inhibition by Kasugamycin of protein synthesis in Piricularia oryzae. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 21(1):73-74 PMID 4970570 |