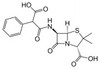
Carbenicillin Disodium, USP is a carboxypenicillin antibiotic routinely used for gene selection. The compound interferes with peptidoglycan synthesis, thus it can also be used to study the role of penicillin-sensitive transpeptidases in the formation of cell walls. The carboxycillins are susceptible to degradation by β-lactamase enzymes.
Carbenicillin Disodium USP conforms to United States Pharmacopoeia specifications.
We also offer:
| Mechanism of Action | Carbenicillin interferes with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to β-lactams is commonly due to cells containing plasmid-encoded β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum | The activity of Carbenicillin is limited to primarily Gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and common enteric bacteria. |
| Microbiology Applications | Carbenicillin Disodium is often used to select for cells that have been transformed with a plasmid containing the ampR gene which confers resistance to ampicillin and Carbenicillin. Carbenicillin Disodium can be substituted for Ampicillin Sodium for better stability and to avoid formation of satellite colonies. Carbenicillin Disodium is a preferred alternative to ampicillin due to its increased stability in the presence of heat and low pH environments. Substituting Carbenicillin Disodium for ampicillin also reduces the risk of satellite colonies appearing on growth media during extended periods of incubation. |
| Plant Biology Applications | Carbenicillin Disodium is routinely used in Agrobacterium mediated transformation protocols to select for resistant Agrobacterium and transformed plants. Carbenicillin Disodium demonstrates low toxicity to plant tissues. RNA-guided genome editing using the CRISPR/Cas9 system was used with tobacco protoplasts and whole-plant transformation. Using multiplexing gRNA, Two genes (NtPDS and NtPDR6) were mutated and transgenic tobacco plants with successfully obtained containing both mutations (Gao et al, 2015). |
| Molecular Formula | C17H16N2Na2O6S |
| References | Bourhis E, Hymowitz SG and Cochran AG (2007) The mitotic regulator Survivin binds as a monomer to its functional interactor Borealin. J. Biol. Chem 282(48):35018-35023 PMID 17881355 Bush K and Bradford PA (2016) B-Lactams and B-Lactamase inhibitors: An overview. Cold Spring Harb.Perspect. Med 6(8): pii: a025247 PMID 27329032 Gao J et al (2015) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Mol. Biol 87(1):99-110 PMID 25344637 Matsuda N, Isuzugawa K, Gao M, Takshina T and Nishimura K. (2004) Development of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system in pear cultivars with low-regeneration Frequency. Hortsci. 39(4) Pitout JD, Sanders CC, Sanders WE (1997) Antimicrobial resistance with focus on beta-lactam resistance in Gram-negative bacilli. Am J Med 103:51-59 PMID 9236486 |
| MIC | Bacillus subtilis (PCI219)| 0.39|| Bacteroides fragilis (ATCC 25285)| >8|| Brucella| ≤4 - 16|| Burkholderia cenocepacia (K56-2)| >1024|| Burkholderia cepacia (CEP509)| >1024|| Burkholderia multivorans (ATCC 17616)| >1024|| Burkholderia stabilis (LMG 14086)| >1024|| Burkholderia vietnamensis (16232)| >1024|| Citrobacter freundii (Basal amp(C))| 1|| Citrobacter freundii (Hyperproducing amp(C))| 128|| Citrobacter freundii (Inducible amp(C))| 1|| Clostridium perfringens (ATCC 13124)| 0.125|| Clostridium spiroforme (A7)| 4|| Clostridium spiroforme (A8)| 4|| Clostridium spiroforme (B61)| 4|| Clostridium spiroforme (BA 1)| 8|| Clostridium spiroforme (C121)| 2|| Clostridium spiroforme (CED 1)| 4|| Clostridium spiroforme (D11)| 8|| Clostridium spiroforme (D13)| 2|| Clostridium spiroforme (D14)| 8|| Clostridium spiroforme (NCTC 11493)| 4|| Clostridium spiroforme (RPO 980)| >8|| Corynebacterium diphtheriae (Tronto)| 1.56|| Enterobacter cloacae (Basal amp(C))| 2|| Enterobacter cloacae (Hyperproducing amp(C))| 256|| Enterobacteriaceae| >8 - >512|| Escherichia coli (0-111)| 1.56|| Escherichia coli (0-143)| 3.13|| Escherichia coli (0-78)| 6.25|| Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922)| 7.81|| Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922)| >8|| Escherichia coli (Basal amp(C))| 2|| Escherichia coli (C921-61)| 16|| Escherichia coli (DH5α + pBC-OXA-46)| 64|| Escherichia coli (DH5α + pBC-SK)| 4|| Escherichia coli (Hyperproducing amp(C))| 16|| Escherichia coli (K-10)| 32|| Escherichia coli (K-12)| 16|| Escherichia coli (K-12)| 25|| Escherichia coli (N43 + acr(A))| 4|| Escherichia coli (N818 + acr(A))| 16|| Escherichia coli (NCTC 10418)| 2|| Escherichia coli (NIHJ JC-1)| 12.5|| Escherichia coli (Umezawa)| 6.25|| Escherichia coli (W4573 + parent)| 2|| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.3 - 18.8|| Klebsiella pneumonia (DT)| 6.25|| Klebsiella pneumonia (SHV-1)| 64|| Klebsiella pneumonia (β-lactamase negative)| 2|| Morganella morganii (Hyperproducing amp(C))| 32|| Morganella morganii (Inducible amp(C))| 1|| Nocardia asteroides| 50 - ≥400|| Proteus mirabilis (IFO 12255)| 1.56|| Proteus mirabilis (IFO 3849)| 3.13|| Proteus morganii (IFO 3168)| 6.25|| Proteus morganii (IFO 3848)| 0.78|| Proteus vulgaris (Hyperproducing amp(C))| 32|| Proteus vulgaris (IFO 3851)| 6.25|| Proteus vulgaris (IFO 3988)| 1.56|| Proteus vulgaris (Inducible amp(C))| 4|| Proteus vulgaris (OX-19)| 50|| Proteus vulgaris (OX-K)| 1.56|| Pseudomonas acidovorans| 128 - 256|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 27853)| 31|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (D363 + pH 6.0)| 25|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (D363 + pH 7.0)| 50|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (D363 + pH 8.0)| 100|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (D363 + pH 9.0)| 100|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (D363)| 50|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (DK101 + streptomycin-resistant + gentamicin-resistant: opr(D))| 64|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (F4980)| 256|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (F66336)| 256|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3007-T)| 200|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3310-T)| 200|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3324-T)| 200|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3325-T)| 200|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3327-T)| 200|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3333-T)| 200|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3338-T)| 400|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3363-T)| 50|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (GN-3365-T)| 100|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (H4563)| >1024|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (LESB58)| 256|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (M18)| 256|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (M22152)| >1024|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (M37310)| 1024|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (M38100A)| 16|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (M38100B)| 1024|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (N18)| 3.13|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (NCTC 10662)| 32|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P8)| 100|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1)| 64|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (SP)| 50|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (T15464)| >1024|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (T2095)| 256|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (T5177)| >1024|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (T6268)| 16|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (U31 + pH 6.0)| 100|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (U31 + pH 7.0)| 100|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (U31 + pH 8.0)| 200|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (U31 + pH 9.0)| 200|| Pseudomonas cepacia| 32 - 512|| Pseudomonas diminuta| 23408|| Pseudomonas flourescens| >32 - >152|| Pseudomonas maltophilia| 16 - 256|| Pseudomonas paucimobilis| 2 - 64|| Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes| 2 - 64|| Pseudomonas putida| >152 - >512|| Pseudomonas putrefaciens| 2 - 64|| Pseudomonas stutzeri| 2 - 64|| Salmonella hirschfeldii| 12.5|| Salmonella Paratyphi (A)| 50|| Salmonella schottmuelleri (Watson)| 6.25|| Salmonella typhi (Boxhill-58)| 6.25|| Salmonella typhi (Watson)| 6.25|| Salmonella typhimurium| 12.5|| Salmonella typhimurium (LT2)| 8|| Serratia marcescens (Hyperproducing amp(C))| 32|| Serratia marcescens (Inducible amp(C))| 4|| Shigella dysenteriae (EW-1)| 3.13|| Shigella flexneri (EW-10)| 12.5|| Shigella flexneri (EW-40)| 12.5|| Shigella sonnei (EW-33)| 3.13|| Staphylococcus aureus (1840 + penicillin-resistant)| 12.5|| Staphylococcus aureus (308 A-1)| 0.78|| Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923)| 1|| Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 35556)| 1|| Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6571)| 0.5|| Staphylococcus aureus (FDA 209P + pH 6.0)| 0.39|| Staphylococcus aureus (FDA 209P + pH 7.0)| 0.39|| Staphylococcus aureus (FDA 209P + pH 8.0)| 0.78|| Staphylococcus aureus (FDA 209P + pH 9.0)| 0.78|| Staphylococcus aureus (FDA 209P)| 0.39|| Staphylococcus aureus (MU50)| 512|| Staphylococcus aureus (N315)| 32|| Staphylococcus aureus (T15)| 3.13|| Staphylococcus aureus (T20)| 3.13|| Staphylococcus aureus (T3)| 0.78|| Staphylococcus aureus (T30)| 0.78|| Staphylococcus aureus (T32)| 6.25|| Staphylococcus aureus (T62)| 3.13|| Staphylococcus aureus (T63)| 3.13|| Staphylococcus aureus (T69)| 3.13|| Staphylococcus aureus (T78)| 6.25|| Staphylococcus aureus (T88)| 3.13|| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia| 32 - >512|| Streptococcus mitior (North America)| 1.56|| Streptococcus pneumonia (type I)| 0.39|| Streptococcus pneumonia (type II)| 0.2|| Streptococcus pneumonia (type III)| 0.2|| Streptococcus pyogenes (Dick)| 0.2|| Streptococcus pyogenes (E-14)| 0.2|| Streptococcus pyogenes (NY-5)| 0.2|| Streptococcus pyogenes (S-8)| 0.2|| Vibrio cholerae (Inaba)| 3.13|| |