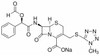
Cefamandole Nafate, USP is a second-generation cephalosporin and beta-lactam antibiotic with bactericidal activity. It is freely soluble in aqueous solution and sparingly soluble in methanol. The ester compound, Nefamandole Nafate is hydrolyzed to Cefamandole.
Cefamandole has been used to study the expression of penicillin-binding proteins on bacterial cell walls and antibiotic resistance mechanisms.
We also offer:
- Cefamandole Sodium (C079)
| Mechanism of Action | Like β-lactams, cephalosporins interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to cephalosporins is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum | Cefamandole is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin targeting a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram- negative bacteria. |
| Impurity Profile | |Cefamandole nafate|42540-40-9|C19H17N6NaO6S2|512.5| |Cefamandole sodium|30034-03-8|C18H17NaO5S2|484.5| Impurity A| formylmandeloyl-7-amino-desacetoxy-cephalosporanic acid||C16H16N2O6S|364.4| Impurity C| O-acetylcefamandole||C18H20N6O6S2|480.5| Impurity D| 1-methyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiol|69713-31-1|C2H4N4S|16.145| Impurity E| formylmandeloyl-7-ACA||C19H18N2O8S|434.4| |
| Microbiology Applications |
Cefamandole Nafate is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
|
| Molecular Formula | C19H17N6NaO6S2 |
| References |
Georgopapadakou NH (1992) Mechanisms of action of Cephalosporin 3'-quinolone esters, carbamates, and tertiary amines in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37(3):559-565. Gupta D, V, Stewart KR (1981) Stability of Cefamandole Nafate and cefoxitin sodium solutions. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 38(6):875-879 PMID 7246563 |
| MIC | Bacillus spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Bacteroides distasonis| ? - ?| 1389| Bacteroides distasonis| >128 - ?| 1473| Bacteroides fragilis| ? - ?| 1389| Bacteroides fragilis| 64 - >128| 1473| Bacteroides fragilis| 32 - ?| 1438| Bacteroides fragilis (ATCC 25285)| 64 - ?| 1438| Bacteroides fragilis (group)| 32 - >128| 1473| Bacteroides fragilis (NCTC 9343)| 8 - ?| 401| Bacteroides fragilis (UC-2)| 32 - ?| 1438| Bacteroides melaninogenicus| ? - ?| 1389| Bacteroides ovatus| ? - ?| 1389| Bacteroides ovatus| >128 - ?| 1473| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| ? - ?| 1389| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 128 - >128| 1473| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron| 32 - ?| 1438| Bacteroides uniformis| 64 - >128| 1473| Bacteroides vulgatus| 32 - >128| 1473| Bifidobacterium spp.| 1 - 64| 1473| Brucella| 4 - >64| 1388| Citrobacter| 0.8 - 1.6| 1418| Citrobacter| 1.63 - >100| 1414| Citrobacter| 100 - ?| 1418| Citrobacter diversus| ? - ?| 1386| Citrobacter diversus| 0.5 - 32| 1434| Citrobacter diversus| ? - ?| 1389| Citrobacter diversus| 1.5 - ?| 1447| Citrobacter freundii| ? - ?| 1386| Citrobacter freundii| ? - ?| 1389| Citrobacter freundii| 0.5 - >128| 1434| Citrobacter freundii| 2.4 - ?| 1447| Citrobacter spp.| 0.12 - 64| 1438| Citrobacter spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Clostridium difficile| ? - ?| 1389| Clostridium difficile| 32 - 128| 1473| Clostridium perfringens| ? - ?| 1389| Clostridium perfringens| 2 - ?| 1438| Clostridium perfringens (ATCC 13124)| 1 - ?| 1438| Clostridium ramosum| 1 - ?| 1438| Clostridium spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Corynebacterium spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Diplococcus pneumoniae| 0.01 - 0.2| 1413| Diplococcus pneumoniae| <0.1 - 0.2| 1414| Enterobacter| 1.6 - 400| 1418| Enterobacter| 1.63 - >100| 1414| Enterobacter| 3.12 - >100| 1414| Enterobacter aerogenes| ? - ?| 1386| Enterobacter aerogenes| 1 - 128| 1438| Enterobacter aerogenes| ? - ?| 1389| Enterobacter agglomerans| 0.5 - 2| 1438| Enterobacter agglomerans| ? - ?| 1389| Enterobacter cloacae| 0.5 - >128| 1434| Enterobacter cloacae| ? - ?| 1386| Enterobacter cloacae| ? - ?| 1389| Enterobacter cloacae| 0.5 - 128| 1438| Enterobacter gergoviae| ? - ?| 1389| Enterobacter spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Enterobacter spp.| 0.25 - 64| 1447| Enterobacter spp.| 0.78 - 25| 1410| Enterobacter spp.| 1.8 - ?| 1447| Enterococci| ? - ?| 1389| Enterococcus aerogenes| 0.5 - >128| 1434| Escherichia coli| ? - ?| 1386| Escherichia coli| 0.25 - 64| 1434| Escherichia coli| ? - ?| 1389| Escherichia coli| ? - ?| 1389| Escherichia coli| 0.12 - 64| 1438| Escherichia coli| 0.2 - 25| 1410| Escherichia coli| 0.25 - 16| 1447| Escherichia coli| ≤0.39 - ?| 1406| Escherichia coli| 0.4 - 12.5| 1414| Escherichia coli| 0.7 - ?| 1447| Escherichia coli| 0.8 - 12.5| 1418| Escherichia coli| 0.8 - >100| 1414| Escherichia coli (1189)| 6.3 - ?| 1418| Escherichia coli (3337)| 12.5 - ?| 1418| Escherichia coli (cephalothin-resistant)| 0.8 - 400| 1418| Escherichia coli (HB101)| 0.5 - ?| 1449| Escherichia coli (NCTC 10418)| 0.2 - ?| 401| Escherichia coli (XL1)| 0.5 - ?| 1449| Eubacterium lentum| 1 - 64| 1473| Eubacterium lentum| 32 - ?| 1438| Fusobacteria| 0.06 - 128| 1473| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.5 - 128| 1473| Fusobacterium mortiferum| 0.5 - ?| 1438| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.06 - 0.125| 1473| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 0.12 - ?| 1438| Fusobacterium nucleatum| 0.125 - 1| 1473| Fusobacterium varium| 8 - 32| 1473| Haemophilus influenzae| 0.06 - 0.25| 1438| Haemophilus influenzae (ESBL)| ? - ?| 1389| Haemophilus influenzae (non-ESBL)| ? - ?| 1389| Herellea| 6.5 - >100| 1414| Klebsiella| 1.6 - 50| 1418| Klebsiella| 200 - ?| 1418| Klebsiella oxytoca| 0.12 - 32| 1434| Klebsiella oxytoca| 1.2 - ?| 1447| Klebsiella pneumoniae| ? - ?| 1386| Klebsiella pneumoniae| ? - ?| 1389| Klebsiella pneumoniae| 0.012 - 128| 1438| Klebsiella pneumoniae| 0.25 - >128| 1434| Klebsiella pneumoniae| 0.2 - 25| 1410| Klebsiella pneumoniae| 0.8 - 50| 1414| Klebsiella pneumoniae| 0.8 - 100| 1414| Klebsiella pneumoniae| 1.5 - ?| 1447| Klebsiella pneumoniae (Gentamicin-resistant)| 1 - >128| 1434| Klebsiella pneumoniae (Gentamicin-susceptible)| 0.25 - 64| 1434| Klebsiella spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Klebsiella spp.| 0.25 - >128| 1447| Lactobacillus spp.| 1 - 64| 1473| Listeria monocytogenes| ? - ?| 1389| Micrococcus spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Morganella morganii| 0.5 - 128| 1434| Morganella morganii| ? - ?| 1389| Morganella spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Neisseria gonorrhoeae (ESBL)| ? - ?| 1389| Neisseria gonorrhoeae (non-ESBL)| ? - ?| 1389| Neisseria gonorrhoeae (penicillin-resistant)| 0.06 - 1| 1408| Neisseria gonorrhoeae (penicillin-susceptible)| 0.002 - 2| 1408| Neisseria meningitidis| 0.03 - 0.25| 1438| Neisseria meningitidis| ? - ?| 1389| Nocardia asteroides| 15.71 - ?| 1406| Ochrobactrum anthropi (SLO74)| >=128 - ?| 1449| Peptococcus asaccharolyticus (ATCC 29743)| 1 - ?| 1438| Peptococcus magnus| 0.12 - ?| 1438| Peptostreptococcus anaerobius| 0.125 - 64| 1473| Peptostreptococcus asaccharolyticus| 0.125 - 64| 1473| Peptostreptococcus magnus| 0.125 - 64| 1473| Peptostreptococcus tetradius| 0.125 - 64| 1473| Porphyromonas| 0.125 - >128| 1473| Porphyromonas asaccharolytica| 0.125 - 128| 1473| Prevotella bivia| 2 - >128| 1473| Prevotella buccae| 0.125 - 128| 1473| Prevotella corporis| 0.125 - 8| 1473| Prevotella disiens| 1 - 128| 1473| Prevotella intermedia| 0.5 - 16| 1473| Prevotella melaninogenica| 2 - >128| 1473| Prevotella oralis| 0.125 - 128| 1473| Prevotella oris| 0.125 - 128| 1473| Propionibacterium acnes | 0.25 - 2| 1473| Propionibacterium spp.| 0.25 - 2| 1473| Proteus (indole-positive)| 1.6 - 400| 1418| Proteus mirabilis| ? - ?| 1386| Proteus mirabilis| ? - ?| 1389| Proteus mirabilis| 0.12 - 4| 1434| Proteus mirabilis| ? - ?| 1389| Proteus mirabilis| 0.2 - 25| 1410| Proteus mirabilis| 0.25 - 32| 1447| Proteus mirabilis| 0.4 - 50| 1414| Proteus mirabilis| 0.5 - ?| 1447| Proteus mirabilis| 0.8 - 50| 1414| Proteus mirabilis| 0.8 - ?| 1418| Proteus mirabilis| 1.6 - 6.2| 1418| Proteus morganii| 0.7 - ?| 1447| Proteus morganii| 1.63 - >100| 1414| Proteus morganii| 100 - ?| 1418| Proteus rettgeri| <0.03 - 16| 1434| Proteus rettgeri| 2.3 - ?| 1447| Proteus rettgeri| 50 - >100| 1414| Proteus spp. (indole-positive)| 0.12 - >128| 1438| Proteus spp. (indole-positive)| 0.25 - >128| 1447| Proteus vulgaris| ? - ?| 1389| Proteus vulgaris| 0.5 - >128| 1434| Proteus vulgaris| ? - ?| 1389| Proteus vulgaris| 0.8 - >100| 1414| Proteus vulgaris| 8.2 - ?| 1447| Providencia| 0.8 - 200| 1418| Providencia| 3.1 - ?| 1418| Providencia rettgeri| ? - ?| 1389| Providencia spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Providencia spp.| 4 - 32| 1438| Providencia spp.| 1 - ?| 1447| Providencia spp. (indole-positive)| 0.25 - >128| 1447| Providencia stuartii| 0.12 - 32| 1434| Providencia stuartii| ? - ?| 1389| Pseudomonas acidovorans| ? - ?| 1389| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| ? - ?| 1389| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| ? - ?| 1386| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| 64 - >128| 1438| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| >128 - ?| 1434| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| >100 - ?| 1414| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| 253.4 - ?| 1447| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 27853)| >128 - ?| 401| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Gentamicin-resistant)| >128 - ?| 1434| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Gentamicin-susceptible)| >128 - ?| 1434| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (NCTC 10662)| >128 - ?| 401| Pseudomonas cepacia| ? - ?| 1389| Pseudomonas cepacia| >100 - ?| 1414| Pseudomonas fluorescens| ? - ?| 1389| Pseudomonas maltophilia| ? - ?| 1389| Pseudomonas putida| ? - ?| 1389| Pseudomonas spp.| ? - ?| 1386| Pseudomonas spp.| 32 - >128| 1447| Pseudomonas spp.| 190.2 - ?| 1447| Pseudomonas stutzeri| ? - ?| 1389| Salmonella| ? - ?| 1386| Salmonella| <0.4 - 0.8| 1414| Salmonella| 0.8 - 200| 1418| Salmonella| <0.8 - ?| 1414| Salmonella spp.| 0.5 - 8| 1438| Salmonella spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Serratia| 12.5 - ?| 1418| Serratia| 25 - 400| 1418| Serratia marcescens| ? - ?| 1386| Serratia marcescens| ? - ?| 1389| Serratia marcescens| 1 - >128| 1438| Serratia marcescens| 4 - >128| 1434| Serratia marcescens| 1 - >128| 1447| Serratia marcescens| 6.5 - >100| 1414| Serratia marcescens| 24.3 - ?| 1447| Serratia marcescens (Gentamicin-resistant)| 4 - >128| 1434| Serratia marcescens (Gentamicin-susceptible)| 16 - >128| 1434| Serratia spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Shigella| 0.8 - 6.5| 1414| Shigella| 0.8 - 25| 1418| Shigella spp.| ? - ?| 1389| Shigella spp.| 2 - ?| 1438| Staphylococcus aureus| ? - ?| 1386| Staphylococcus aureus| 0.25 - 8| 1438| Staphylococcus aureus| ? - ?| 1389| Staphylococcus aureus| <0.1 - 1.6| 1414| Staphylococcus aureus| ≤0.39 - ?| 1406| Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6571)| 0.25 - ?| 401| Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-resistant)| ? - ?| 1389| Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible)| ? - ?| 1389| Staphylococcus aureus (penicillin-resistant)| 0.2 - 12.5| 1410| Staphylococcus aureus (penicillin-susceptible)| 0.2 - 0.78| 1410| Staphylococcus epidermidis| ? - ?| 1386| Staphylococcus epidermidis| ? - ?| 1389| Staphylococcus epidermidis| 0.1 - 0.8| 1414| Staphylococcus pyogenes| 0.03 - 0.06| 1438| Staphylococcus saprophyticus| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococci (group D)| 0.12 - 64| 1438| Streptococcus agalactiae| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococcus bovis| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococcus faecalis| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococcus faecalis| 25 - ?| 1414| Streptococcus pneumoniae| 0.015 - 0.12| 1438| Streptococcus pneumoniae| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococcus pneumoniae| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococcus pneumoniae| 0.2 - ?| 1410| Streptococcus pyogenes| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococcus pyogenes| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococcus pyogenes| <0.1 - 0.8| 1414| Streptococcus pyogenes| 0.2 - 0.78| 1410| Streptococcus viridans| ? - ?| 1389| Streptococcus viridans| <0.1 - 0.1| 1414| |