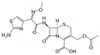
Cefotaxime Sodium, CulturePure is a broad-spectrum, third-generation, β-lactamase-resistant cephalosporin antibiotic. The product is ≥99.0% pure and is uniquely designed for cell/plant culture applications. It has been carefully tested to make sure it does not exhibit toxicity against routine cell lines or plant cells, and purification technology has removed E-cefotaxime (an isoform that is toxic to plant cells).
Cefotaxime was discovered in 1976, and came into commercial use in 1980. It interferes with bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis. Cefotaxime is metabolized in vivo to desacetylcefotaxime, a less potent derivative but also microbiologically active and more stable against selected β-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms.
Cefotaxime Sodium, CulturePure is freely soluble in aqueous solution.
| Mechanism of Action | Like β-lactams, cephalosporins interfere with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBP’s are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues providing additional strength to the cell wall. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised and ultimately leads to cell lysis and death. Resistance to cephalosporins is commonly due to cells containing plasmid encoded β-lactamases. Cefotaxime Sodium however, is largely resistant to β-lactamases. |
| Spectrum | Cefotaxime sodium has broad spectrum activity against a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. However, unlike many cephalosporin antibiotics, Cefotaxime Sodium is not effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In addition, Cefotaxime blocks the division of cyanobacteria. |
| Microbiology Applications | Cefotaxime Sodium is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against gram positive and gram negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options for infected patients. Representative MIC values include:
|
| Plant Biology Applications |
Agrobacterium-mediated transformation is one of the well-established techniques for introducing foreign DNA into plant tissues. Explants are co-cultivated with disarmed Agrobacterium carrying the gene of interest. Cefotaxime is the only cephalosporin with low toxicity to plants, even at higher concentrations (up to 500 mg/L). Cefotaxime is often used in Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation to combat bacterial growth. It is also sometimes used in combination with vancomycin as it has a synergistic effect. During transformation with soybean, treatment with Cefotaxime at 350 and 500 mg/L efficiently suppressed Agrobacterium for 49 days. When it was used in combination with Vancomycin (250 mg/L each), this combination suppressed Agrobacterium for 63 days with minimal phytotoxicity. Cefotaxime was superior to Carbenicillin at eliminating Agrobacterium from soybean somatic embryo clusters (Wiebke et al, 2006). Cefotaxime (100 mg/l) promoted embryogenesis in microspore culture of wheat and triticale, and enhanced cell growth and green plant production (Asif et al, 2013). |
| Molecular Formula | C16H16N5NaO7S2 |
| References |
Asif M et al (2013) Cefotaxime prevents microbial contamination and improves microspore embryogenesis in wheat and triticale. Plant Cell Rep. 32(10):1637-1646 PMID 23896731 Dudley MN and Barriere SL (1982) Cefotaxime: Microbiology, pharmacology, and clinical use. Clin. Pharm. 1(2):114-124 PMID 6309465 Fischer J, Ganelli CR (2006) Analogue-based drug discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 494. ISBN 9783527607495 Georgopapadakou NH (1992) Mechanisms of action of cephalosporin 3'-quinolone esters, carbamates, and tertiary amines in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 37(3): 559-65 Mathias RJ and Boyd LA (1986) Cefotaxime stimulates callus growth, embryogenesis and regeneration in hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em Thell). Plant Sci. 46:217-223 Molinari G, Saverino D, Paglia P, Debbia EA, Schito GC (1991) Synergistic antibacterial interaction of Cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime. J Chemother. 3(1):6-12 PMID 2019866 Wiebke B et al (2006) Influence of antibiotics on embryogenic tissue and Agrobacterium tumefaciens suppression in soybean genetic transformation. Bragantia 65(4) ISSN 1678-4499 |