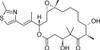
Epothilone B is a microtubule inhibitor isolated from the myxobacteria, Sorangium cellulosum.
Epothilone B is soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO. Poor water solubility.
| Mechanism of Action | Epothilone B acts by stabilising microtubule formation at the taxol binding site, and causes cell cycle arrest at the G2/M transition, leading to cytotoxicity. |
| References | Epothilons A and B: Antifungal and cytotoxic compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (myxobacteria) production, physico-chemical and biological properties. Gerth K. et al. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1996, 49, 560. Epothilones, a new class of microtubule-stabilizing agents with a taxol-like mechanism of action. Bollag D. M. et al. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 2325. |