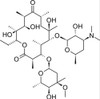
Erythromycin A, EvoPure is a highly purified form of the macrolide antibiotic Erythromycin A and is a natural product. Erythromycin is composed of Erythromycin A, B, C, D, and additional impurities. Erythromycin A is the most active component.
For other Erythromycin products, click here.
| Application | Erythromycin A, EvoPure can be used as a reference standard or to study the individual properties of Erythromycin A. Reference standards are well characterized, highly pure compounds that can be used to help identify and/or quantify impurities in pharmaceutical compounds and antimicrobials. |
| Mechanism of Action | Macrolide antibiotics inhibit bacterial growth by targeting the 50S ribosomal subunit of the 70S ribosome preventing aminoacyl translocation of the A-site to P-side and peptide bond formation during protein synthesis. Resistance to Erythromycin is commonly attributed to mutations in 50S rRNA preventing erythromycin binding allowing the cell to synthesize proteins free of error. In acidic aqueous media, Erythromycin A is degraded via intramolecular dehydration to form erythromycin-6,9-hemiketal and then anhydroerythromycin, both of which possess little antimicrobial activity (Fiese and Staffen, 1990). |
| Spectrum | Effective against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | The production of bioactive compounds in heterologous hosts has become a valuable tool for the investigation of biosynthetic pathways. The reconstruction of the Erythromycin A biosynthetic pathway was done in E. coli (Zhang et al, 2010). The biosynthesis of 6-deoxyerythronolide B (6-dEB), the macrocyclic core of Erythromycin A, in an engineered strain of E. coli was described (Pfeifer et al., 2001). |
| Molecular Formula | C37H67NO13 · 2H2O |
| References | Fiese EF and Staffen SH (1990) Comparison of the acid stability of azithromycin and Erythromycin A. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 25(A):39-47 Kibwage IO et al (1985) Antibacterial activities of Erythromycins A, B, C, and D and some of their derivatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 28(5):630-33 Weber T et al (2010) Making E. coli an Erythromycin production plant. Chem. & Biol. 17(11):1168-1169 Zhang H et al (2010) Complete biosynthesis of Erythromycin A and designed analogs using E. coli as a heterologous host. Chem. & Biol. 17(11):1232-1240 |
| MIC | Enterococcus (erythromycin A-resistant)| 64 - ≥512|| Enterococcus (erythromycin A-susceptible)| ≤0.06 - 4|| Enterococcus (penicillin-resistant)| 0.5 - ≥512|| Enterococcus (penicillin-susceptible)| ≤0.006 - ≥512|| Enterococcus (van(A))| ≥512|| Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 9212)| 1.56|| Enterococcus faecium (ATCC 19434)| 3.13|| Haemophilus influenzae| ≤0.12 - >8|| Haemophilus influenzae (0131)| 2|| Haemophilus influenzae (ATCC 43095)| 6.25|| Haemophilus influenzae (ESBL)| ≤0.12 - >8|| Haemophilus influenzae (HTM)| 2 - >16|| Haemophilus influenzae (MHF)| 2 - >16|| Haemophilus influenzae (non-ESBL)| ≤0.12 - >8|| Legionella spp.| 0.06 - 0.5|| Moraxella catarrhalis| ≤0.12 - 0.5|| Moraxella catarrhalis (HTM)| 0.125 - 0.5|| Moraxella catarrhalis (MHF)| 0.125 - 0.5|| Mycoplasma fermentans| ≥64|| Mycoplasma genitalium| ≤0.015|| Mycoplasma hominis| ≥64|| Mycoplasma penetrans| 2|| Mycoplasma pneumonia| ≤0.015|| Staphylococcus aureus (erm(C))| >100|| Staphylococcus aureus (mrsA)| 100|| Staphylococcus aureus (Smith)| 0.2|| Staphylococcus pneumonia (erm(B))| >100|| Staphylococcus pneumonia (ery(S))| 0.03|| Staphylococcus aureus (Ery S)| <0.2|| Staphylococcus pyogenes (ery(S))| <0.13|| Staphylococcus pneumonia (mef(E))| >13|| Staphylococcus pyogenes (erm(B))| 64|| Staphylococcus pyogenes (mef(A))| 8|| Streptococcus pneumonia| ≤0.12 - >100|| Streptococcus pneumonia (erythromycin A-resistant)| 1 - >8|| Streptococcus pneumonia (erythromycin A-susceptible)| ≤0.12 - 0.25|| Streptococcus pneumonia (IID553)| 0.1|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-intermediate + erythromycin-intermediate)| 8 - ≥32|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-intermediate + erythromycin-resistant)| 8 - ≥32|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-intermediate + erythromycin-susceptible)| 0.06 - 0.25|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-intermediate)| ≤0.12 - >8|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-resistant)| ≤0.12 - >8|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-susceptible + erythromycin-intermediate)| 1 - ≥32|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-susceptible + erythromycin-resistant)| 1 - ≥32|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-susceptible + erythromycin-susceptible)| 0.06 - 0.5|| Streptococcus pneumonia (penicillin-susceptible)| ≤0.12 - >8|| Streptococcus pyogenes (erm(B))| <32 - ?|| Streptococcus pyogenes (ermTR)| 1 - 2|| Streptococcus pyogenes (erythromycin A-susceptible)| 0.003 - 0.25|| Streptococcus pyogenes (mef(A))| 4 - 8|| Ureaplasma urealyticum (doxycycline-resistant)| 0.12 - 1|| Ureaplasma urealyticum (doxycycline-susceptible)| 0.12 - 1|| |