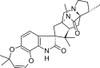
Paraherquamide E is a member of the paraherquamide family which causes a potent non-toxic paralysis of nematodes and has led to investigation as potential anthelmintics. Although paraherquamide A has received more attention, paraherquamide E is the more potent anthelmintic in vivo. Paraherquamide E was found to be the most potent of a series of paraherquamide analogues tested for insecticidal activity against a hemipteran, with an LD50 of 0.089 μg/nymph.
| Molecular Formula | C28H35N3O4 |
| References | Insecticidal activity of paraherquamides, including paraherquamide H and paraherquamide I, two new alkaloids isolated from Penicillium cluniae. Lopez-Gresa M.P. et al. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2921. Paraherquamide and 2-deoxy-paraherquamide distinguish cholinergic receptor subtypes in Ascaris muscle. Robertson A.P. et al. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 853. et al. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 492. New paraherquamide antibiotics with anthelmintic activity. Blanchflower S.E. Novel antinematodal and antiparasitic agents from Penicillium charlesii. I. Fermentation, isolation and biological activity. Ondeyka J.G. J. Antibiot. 1990, 43, 1380. Novel antinematodal and antiparasitic agents from Penicillium charlesii. I. Fermentation, isolation and biological activity. Ondeyka J.G. J. Antibiot. 1990, 43, 1380. |