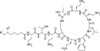
Polymyxin B Sulfate, USP is a polypeptide antibiotic mixture composed of Polymyxins B1, B2, and B3 fractions, with B1 and B2 fractions comprising the majority of the mixture. Polymyxin B components are structurally identical with the exception of a variable fatty acid group on each fraction. Results from in vitro studies have shown marginal differences in MIC data when comparing the fractions. Polymyxin B Sulfate is freely soluble in aqueous solution (25 mg/mL).
Polymyxin B Sulfate, USP conforms to United States Pharmacopoeia specifications.
We also offer:
- Polymyxin B1 Sulfate, EvoPure® (P037)
- Polymyxin B1-I Sulfate, EvoPure® (P038)
- Polymyxin B2 Sulfate, EvoPure® (P039)
- Polymyxin B3 Sulfate, EvoPure® (P040)
- Polymyxin B6 Sulfate, EvoPure® (P054)
- Polymyxin E1 Sulfate, EvoPure® (P055)
- Polymyxin E2 Sulfate, EvoPure® (P056)
- Polymyxin B ReadyMadeTM Solution (P174)
EvoPure® products are purified single antibiotic fractions, most are >99% pure. Highly pure EvoPure® Polymyxin products can be used to analyze the specifc effects of individual Polymyxin B fractions.
| Mechanism of Action | Polymyxin B targets and alters the permeability of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) found in Gram-negative bacteria leading to lysing of the cell. Polymyxin B only needs to interact with LPS, it is not required to enter the cell. |
| Spectrum | Polymyxin B Sulfate targets the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa. |
| Impurity Profile | Polymyxin B1||4135-11-9|C56H98N16O13|1204| Polymyxin B2|||C55H96N16O13|1190| Polymyxin B3|||C55H96N16O13|1190| Polymyxin B1-I|||C56H98N16O13|1204| |
| Microbiology Applications | Polymyxin B Sulfate is commonly used in clinical in vitro microbiological antimicrobial susceptibility tests (panels, discs, and MIC strips) against Gram-negative microbial isolates. Medical microbiologists use AST results to recommend antibiotic treatment options. Representative MIC values include:
Media Supplements:Polymyxin B is routinely used as a selection agent in several types of isolation media: Perfringens agar - Supplement A and Supplement B Perfringens Agar - SFP and TSC Selective Supplements Columbia Blood Agar - Campylobacter Selective Supplement (Skirrow) Columbia Blood Agar - Campylobacter Selective Supplement (Blaser-Wang) Brucella medium - Brucella Selective Supplement MYP Agar - Polymyxin B Bacillus Selection Supplement Legionella CYE Agar - Legionella BMPA-α Selective Supplement Legionella CYE Agar - Legionella MWY Selective Supplement Campylobacter Agar - Campylobacter Selective Supplement (Preston) PALCAM Agar - PALCAM Selective Supplement Legionella CYE Agar - Legionella GVPC Selective Supplement m-CP Medium - Membrane C. perfringens Selective Supplement Burkholderia cepacia Agar Base - Burkholderia cepacia Selective Supplement ORSAB - ORSAB Selective Supplement Campylobacter Agar Base - Modified Preston Campylobacter Selective Supplement Brucella Medium Base - Modified Brucella Selective Supplement Legionella CYE Agar - Legionella GVPN Selective Supplement ChromogenicListeria Agar - Chromogenic Listeria Selective Supplement ChromogenicBacillus cereus Agar - Chromogenic Bacillus cereus Selective Supplement ChromogenicListeria Agar - Chromogenic Listeria Differential Supplement |
| Plant Biology Applications | Polymyxin B Sulfate was successfully tested to counteract phytopathogenic Gram-negative bacterial growth including different strains of Pseudomonas viridiflava and Erwinia carotovora. Polymixin B Sulfate was shown to reduce bacterial growth of different strains of Pseudomonas viridiflava at low concentrations, (0.08 µg/ml) and Erwinia carotovora growth at slightly higher concentrations (0.25 µg/ml) (Selim et al. 2005). Polymyxin B has been shown to elict alkaloid accumulation in E. californica. Treatment at 0.04 mg/ml for 4 hours showed a 5.5x increase in Jasmonate levels. |
| References |
Kassamali et al used Polymyxin B1, Polymyxin B2, Polymyxin B3, and Polymyxin B1-I (TOKU-E) to test for synergistic and antagonistic effects against various Gram-negative organisms in: "Microbiological assessment of Polymyxin B components tested alone and in combination" Crass et al used Polymyxin B1 and B2 (TOKU-E) to investigate the pharmacokinetics of Polymyxin B in: Pharmacokinetics of Polymyxin B in hospitalized adults with cystic fibrosis. Cao G et al (2009) Development and validation of a reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography assay for Polymyxin B in human plasma. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 62(5):1009-1014 PMID 18765414 Mueller MJ, Brodschelm W, Spannagl E and Zenk MH (1993) Signaling in the elicitation process is mediated through the octadecanoid pathway leading to jasmonic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90(16):7490-7494 PMID 11607420 Newton BA (1956) The properties and mode of action of the Polymyxins. Bacter. Rev. 20(1):14-27 PMID 13303920 Orwa JA et al (2001) Isolation and structural characterization of Polymyxin B components. J Chromatogr A 912(2):369-373 PMID 11330807 Selim S, Negrel J, Govaerts C, Gianinazzi S and Tuinen van D (2005) Isolation and partial characterization of antagonistic peptides produced by Paenibacillus sp. strain B2 isolated from the sorghum Mycorrhizosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71(11):6501–6507 PMID 16269674 Zavascki AP, Goldani LA, Li J and Nation RL (2007) Polymyxin B for the treatment of multidrug-resistant pathogens: A critical review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 60(6):1206-1215 PMID 17878146 Tam VH, Cao H, Ledesma, KR, Hu M (2011) In vitro potency of various Polymyxin B components.55(9):4490-491 PMID 21709096
|
| MIC | Diplococcus pneumoniae| ≥400|| Fusobacterium necrophorum| 8.1 - 100|| Haemophilus influenzae| ≥0.8|| Pseudomonas aeruginosa| 0.25 - 1|| |