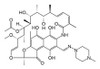
Rifampicin ReadyMade™ Solution is a sterile-filtered solution of Rifampicin dissolved in water at a concentration of 10 mg/ml. This aqueous formulation has been solubilized with starch and is safer than DMSO or methanol. For usage, simply simply add 1-3 ml to each liter of your culture medium. Rifampicin Solution is non-toxic to plant cells.
Rifampicin (syn: Rifampin) is a semisynthetic antimicrobial derived from Rifamycin SV and originally developed by the Lepetit group in 1965. It has activity against Gram-positive bacteria, some Gram-negative anaerobic bacteria, protozoa, fungi, and poxviruses. It can be used in tuberculosis research.
We also offer:
| Mechanism of Action |
Rifampicin targets prokaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerases which prevent subsequent RNA transcription and protein translation. Bacterial resistance to Rifampicin is caused by mutations leading to a change in the structure of the β subunit of RNA polymerase. Rifampicin inhibits the assembly of DNA and protein into mature virus particles. It inhibits initiation of RNA synthesis by binding to the β subunit of RNA polymerase, which results in cell death. Rifampicin has been shown to inhibit αsynuclein fibrillation and disaggregate fibrils in a concentration-dependent manner. Rifampicin can activate pregnane X receptor (PXR), which affects cytochrome P450, and the activity of glucuronosyltransferases and P-glycoprotein. Rifampicin has been shown to enhance CYP2C-mediated metabolism, affect compounds that are transported by P-glycoprotein and metabolized by CYP3A4. |
| Spectrum | Rifampicin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic with a wide range of activity including:
|
| Microbiology Applications | Rifampicin is commonly used in bacterial recombinant protein expression to inhibit bacterial RNA polymerase activity and synthesis of host bacterial proteins. Rifampicin can also be used as a selective agent to isolate Campylobacter jejuni. Rose et al. used Rifampicin (TOKU-E) in methacrylate-based copolymer films and studied its effects on biofilm formation in: "Prevention of biofilm formation by methacrylate-based copolymer films loaded With Rifampin, Clarithromycin, Doxycycline alone or in combination. |
| Plant Biology Applications | Rifampicin has been tested in Jerusalem artichoke tuber explants by adding 10- 50 µg/ml to the tissue culture medium. At 50 µg/ml no bacterial infection was detectable, without affecting cell division rates, cytodifferentiation and DNA synthesis (Philips, 1981). |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications |
Rifampicin has been shown to have immunosuppressive effects in mice. Rifampicin has been shown to inhibit α-synuclein fibrillation and disaggregate fibrils in a concentration-dependent manner. Rifampicin can activate pregnane X receptor (PXR), which affects cytochrome P450, and the activity of glucuronosyltransferases and P-glycoprotein. Rifampicin has been shown to enhance CYP2C-mediated metabolism, affect compounds that are transported by P-glycoprotein and metabolized by CYP3A4. |
| Molecular Formula | C43H58N4O12 |
| References |
Bassi L, Berardino L, Arioli V, Silvestri L and Lignière E (1973). Conditions for immunosuppression by Rifampicin. J. Infect. Dis 128(6), 736-744 Li T and Chiang JY (2006) Rifampicin induction of CYP3A4 requires pregnane X receptor cross talk with hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha and coactivators, and suppression of small heterodimer partner gene expression. Drug metabolism and disposition: the biological fate of chemicals, 34(5):756-764 Maddison JE, A Watson DJ, Elliott D (2008) Chapter 8 - Antibacterial drugs. Sm. Animal Clin. Pharmacol. (2nd ed):148-185 Philips R, Arnott SM and Kaplan SE (1981) Antibiotics in plant tissue culture: Rifampicin effectively controls bacterial contaminants without affecting the growth of short-term explant cultures of Helianthus tuberosus. Plant Sci. Lett. 21(3):235-240 |