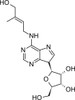
Trans-Zeatin-Riboside is a naturally occurring cytokinin and plant growth regulator routinely used in plant tissue culture to induce shoot formation. Zeatins were discovered in immature Zea mays and occurs in many plant extracts and is the active ingredient in coconut milk. It has two isomers: cis and trans, but the trans isomer is considered more active. Recently, it has been shown that cytokinins like Zeatin function in plant immunity. With pesticides having a negative impact on human health and resistance on the rise, the practical impact of cytokinin-mediated resistance could complement crop protection efforts for added food safety and harvest yield.
Trans-Zeatin-Riboside is soluble in alkaline solutions.
We also offer:
- Trans-Zeatin (Z005)
| Mechanism of Action | trans-Zeatin functions differently depending on which plant system is involved. In Arabidopsis, it functions via high-affinity receptors, include histidine kinases (AHK). Cytokinins have also been shown to moderate plant immunity. For moderating the defense mechanism to pathogens in Arabidopsis, the response is based on salicylic acid-dependent translational control. However in tobacco, cytokinins (specifically Zeatin) were found to mediate resistance against infection in tobacco via increased antimicrobial phytoalexin synthesis independent of salicylic acid signaling (Grosskinsky et al, 2011). The phytoalexins produced were scopoletin and capsidiol, and these were able to substitute for the cytokinin signal. |
| Cancer Research Applications | Cytokinin ribosides have shown to have anticancer activity both in vitro and in vivo, seen from a panel of human cancer cell lines. Structural requirements for their cytotoxic activity against human cancer cell lines differ from their requirements in plant bioassays (Voller et al, 2010). |
| Plant Biology Applications | Cytokinins such as trans-Zeatin are used in plant tissue culture to regulate cell division and development, promoting cell division and shoot formation. Cytokinins have also been shown to help plants better cope with environmental stress. They are also involved in nutrient mobilization, apical dominance and seed germination.
Cytokinins have shown to be involved in plant immunity, mainly to (hemi)biotrophic but also to necrotrophic pathogens. Research has shown that the cis and trans isoforms differentially modulate plant immunity. Both were studied with tobacco-Pseudomonas syringae pv tabaci (Pst) interaction, a well-established pathosystem to analyze cytokinin effects on plant immunity (Grosskinsky et al, 2005). In the tobacco system, trans-Zeatin was more active than cis-zeatin but both were able to modulate plant immunity. In the tobacco system, the cytokinin-induced resistance is mediated by increased synthesis of two major antimicrobial phytoalexins (scopoletin and capsidiol). This resistance was substantiated by three independent transgenic approaches: a novel pathogen-inducible expression system to induce endogenous CK biosynthesis, and two different ways of exogenously supplying cytokinins. They also used the synthetic 4xJERE promoter which proved to be valuable tool to dissect the role of cytokinins from indirect effects like the developmental stage or metabolic status. Authors took care to analyze at least 1500 replicate leaves, reflecting more than 62000 infection sites to demonstrate the reproducibility and robustness of the pathogen resistance (Grosskinsky et al, 2011). |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | Zeatin can promote anti-aging on human skin fibroblasts, acting optimally at 80 µM. Serial passaging in the presence of Zeatin prevented cell enlargement, reduced intracellular debris, prevented actin polymerization, and enhanced the cell’s ability to decompose hydrogen peroxide and cope with oxidative stress without inducing additional cell proliferation (Rattan and Sodagam, 2005). |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21N5O5 |
| References |
Davey JE and Van Staden J (19760 Cytokinin translocation: Changes in Zeatin and Zeatin-riboside levels in the root exudate of tomato plants during their development. Planta 130:69-72 Grosskinsky DK, Edelsbrunner K, Pfeifhofer H, van der Graaff E, Roitsch T (2005) Cis - and trans-Zeatin differentially modulate plant immunity. Plant Signal Behav. 2013 8(7):e24798 PMID 23656869 Grosskinsky DK et al (2011) Cytokinins mediate resistance against Pseudomonas syringae in tobacco through increased antimicrobial phytoalexin synthesis independent of salicylic acid signaling. Plant Physiol. 2011 Oct;157(2):815-30 PMID 21813654 Ha S and Vankova R (2012) Cytokinins: Metabolism and function in plant adaptation to environmental stresses. Trends Plant Sci. 3(172):172-179 Ishii Y, Hori Y, Sakai S and Honma Y (2002) Control of differentiation and apoptosis of hman myeloid leukemia cells by cytokinins and cytokinin nucleosides, plant redifferentiation-inducing hormones. Cell Growth and Differen. 13:19-26 Rattan SI and Sodagam L (2005) Gerontomodulatory and youth-preserving effects of Zeatin on human skin fibroblasts undergoing aging in vitro. Rejuvenation Res. 8(1):46-57 PMID 15798374 Voller J et al (2010) Anticancer activity of natural cytokinins: A structure-activity relationship study. Phytochem. 71(11-12): 1350-1359 PMID 20553699 |