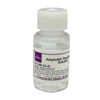
Ampicillin ReadyMadeTM solution is provided as a sterile-filtered solution of Ampicillin Anhydrous formulated in DMSO at a concentration of 100 mg/ml. It has been filter-sterilized using a 0.22 μm filter.
Ampicillin Anhydrous is a member of the β-lactam family similar in structure to penicillin.
We also offer:
- Ampicillin Trihydrate, USP (A009)
- Ampicillin/Sulbactam (2:1)(A071)
- Ampicillin Anhydrous (A043)
- Ampicillin Sodium (A042)
- Ampicillin Trihydrate, EP (A020)
| Mechanism of Action | Like all β-lactams, Ampicillin interferes with PBP (penicillin binding protein) activity otherwise involved in the final phase of peptidoglycan synthesis. PBPs are enzymes which catalyze a pentaglycine crosslink between alanine and lysine residues. Without a pentaglycine crosslink, the integrity of the cell wall is severely compromised ultimately leading to cell lysis. |
| Spectrum | Ampicillin is broad-spectrum, effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria including Gram-negative non-ESBL (Extended Spectrum β-lactamase) bacteria including Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species and medically important enteric pathogens such as Shigella and Salmonella. Interestingly, Ampicillin has been found to be effective against certain β-lactam sensitive VRE or vancomycin resistant Enterococcus; a glycopeptide antibiotic resistant "superbug." Resistance to Ampicillin is routinely used as a selectable marker to confirm successful cell transformation. |
| Microbiology Applications | Ampicillin Anhydrous can be used as a selective agent in several types of isolation media:
Aeromonas Medium Base - Ampicillin Selective Supplement |
| Eukaryotic Cell Culture Applications | Ampicillin is routinely used to select for cells containing the pcDNA3.1 and pEAK10 resistance plasmids in cell line A904L at an effective concentration of 50 µg/mL. For additional information, please visit our cell-culture database. |
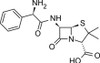
| Molecular Formula | C16H19N3O4S (Ampicillin Anhydrous) |
| References |
Pitout JD, Sanders CC, Sanders WE (1997) Antimicrobial resistance with focus on beta-lactam resistance in Gram-negative bacilli. Am. J. Med 103(1):51-59 PMID 9236486 Waxman DJ and Strominger JL (1983) Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Ann. Rev. Biochem 52:825-869 PMID 6351730 Yang W, Zhang L, Lu Z, Tao W, Zhai Z (2001) A new method for protein coexpression in Escherichia coli using two incompatible plasmids. Protein. Expr. Purif. 22(3):472-478 PMID 11483011 Cure E, Kucuk A and Cure MC (2020) Cyclosporine therapy in cytokine storm due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Rheumatol. Int. 40:1177-1179 Homan KA et al (2016) Bioprinting of 3D convoluted renal proximal tubules on perfusable chips. Sci Rep. 11(6):34845 PMID 27725720 Laupacis A et al (1982) Cyclosporin A: A powerful immunosuppressant. Can. Med Assoc. J 126(9):1041-1046 PMID 7074504 Zhang G and Lyons JG (2002) Cyclosporin A improves the selection of cells transfected with the Puromycin acetyltransferase gene. Biotechniques, 33(1):32-36 |