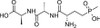
Bialaphos ReadyMadeTM Solution is a sterile-filtered (0.2 μm) solution of Bialaphos Sodium that has been dissolved in water at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. Bialaphos Sodium is a tripeptide antibiotic consisting of two L-alanyl units attached to L-phosphinothricyl. It is used as a nonselective postemergent herbicide. The product is commonly used for gene selection in cereals, and is a bar gene selective agent. Bialaphos Sodium can also be used in molecular biology to select genetically engineered cell lines containing the resistance gene. It has also been used in yeast genetics studies, and as a reference standard for environmental monitoring.
We also offer:
- Bialaphos Sodium (B013)
| Mechanism of Action |
Bialaphos acts as a proherbicide by separating into individual subunits of alanylalanine and phosphinothricin. Phosphinothricin is toxic to cells as it triggers the accumulation of ammonia, thus inhibiting photosynthesis and glutamine synthesis. |
| Spectrum | Bialaphos is a broad-spectrum herbicide that also has activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and certain fungi. |
| General Applications | Bialaphos can be used as a standard for metabolite and environmental contaminant determination in laboratory settings. |
| Microbiology Applications |
Bialaphos Sodium (TOKU-E) was used to study its effects on oligopeptide transporters in a Sinorhizobium meliloti hfq mutant (Sobrero et al, 2011). The pat gene from Streptomyces viridochromogenes confers resistance to Bialaphos, and it is often incorporated in yeast genetics. Yeast cells that carry the pat resistance gene can grow, and resistance is a dominant trait. This dominant resistance trait is useful when studying wild yeast strains. |
| Plant Biology Applications |
Bialaphos is used in transformation of cereals including wheat, rice, maize, barley, sorghum, oat and rye. The bar gene is incorporated in the plant genome along with the gene of interest. When Bialaphos is applied, only plants which are successfully transformed survive. It is more effective than glufosinate. Once inside the plant cell, bialaphos is hydrolyzed and converted to phosphonothricin via the phosphinothricin acetyl transferase enzyme. Phosphinothricin is toxic to plants, causing build up of ammonia, which in turn inhibits glutamine synthetase. |
| Molecular Formula | C11H21N3O6S2P · Na |
| References |
Aragão FJL and Brasileiro ACM (2001) Positive, negative and marker-free strategies for transgenic plant selection. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 14(1):1-10 Dedicova B, Bermudez C, Prias M, Zuniga E, Brondani C (2015) High-throughput transformation pipeline for a Brazilian japonica rice with bar gene selection. Protoplasma 252(4):1071-83 PMID 25488347 Imai S et al (2012) Conversion of Bialaphos to other oligopeptides containing phosphinothricin by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J. Antibiotics 44 (9):1006-1012 Sobrero P et al (2012) Quantitative proteomic analysis of the Hfq-regulon in Sinorhizobium meliloti. PLoS One 7(10):e48494 PMID 23119037 |